A complicated new menace has emerged within the cybersecurity panorama that represents a major evolution in malware improvement.
The LAMEHUG malware household, first recognized by CERT-UA in July 2025, marks a regarding development in cyber assault methodology by integrating synthetic intelligence immediately into its operational framework.
Not like conventional malware that depends on static, pre-programmed directions, LAMEHUG leverages massive language fashions hosted on Hugging Face to dynamically generate instructions for reconnaissance, information theft, and system manipulation in real-time.
This modern method transforms how malicious software program operates by enabling assaults that may adapt their conduct based mostly on the particular setting they encounter.
The malware targets Home windows environments by way of rigorously crafted spear-phishing campaigns, disguising itself as legit functions reminiscent of AI picture mills or canvas instruments.
As soon as deployed, LAMEHUG systematically harvests delicate data together with credentials, system configurations, and paperwork whereas constantly evolving its assault patterns to evade detection mechanisms.
LAMEHUG Primary() and LLM_QUERY_EX Thread (Supply – Splunk)
Splunk analysts recognized that LAMEHUG’s deployment technique includes refined social engineering strategies, presenting itself by way of filenames like “AI_generator_uncensored_Canvas_PRO_v0.9.exe” and “AI_image_generator_v0.95.exe” to capitalize on present curiosity in AI-powered functions.
The LLM Question Setup of LAMEHUG (Supply – Splunk)
The malware’s skill to generate contextually acceptable instructions by way of LLM queries makes it notably harmful, as it could adapt to completely different system configurations and safety measures with out requiring updates from its operators.
Dynamic Command Technology By way of LLM Integration
Probably the most distinctive characteristic of LAMEHUG lies in its unprecedented use of huge language fashions to generate malicious instructions dynamically.
The malware connects to the Qwen 2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct mannequin by way of HuggingFace’s API infrastructure, basically weaponizing legit AI companies for malicious functions.
This integration happens by way of the LLM_QUERY_EX() perform, which constructs particular prompts designed to elicit Home windows administrative instructions from the AI mannequin.
The malware operates by sending rigorously crafted prompts that instruct the LLM to behave as a “Home windows methods administrator” and generate instructions for particular malicious goals.
For system reconnaissance, LAMEHUG prompts the AI to create instructions that set up the listing “C:ProgramDatainfo” and collect complete system data together with {hardware} specs, operating processes, community configurations, and Energetic Listing area particulars, all consolidated right into a single textual content file.
def LLM_QUERY_EX():
immediate = {
‘messages’: [
{
‘role’: ‘Windows systems administrator’,
‘content’: ‘Make a list of commands to create folder C:Programdatainfo and to gather computer information,
hardware information, process and services information, networks information, AD domain information, to execute in
one line and add each result to text file c:Programdatainfoinfo.txt. Return only commands, without markdown’}],
‘temperature’: 0.1,
‘top_p’: 0.1,
‘mannequin’: ‘Qwen/Qwen2.5-Coder-32B-Instruct’ }
For information assortment, the malware points subsequent prompts requesting instructions to recursively copy workplace paperwork, PDFs, and textual content information from consumer directories together with Paperwork, Downloads, and Desktop folders to the centralized assortment level.
The AI-generated responses make the most of Home windows utilities reminiscent of systeminfo, wmic, whoami, and dsquery for reconnaissance, whereas xcopy.exe facilitates doc harvesting throughout a number of folder paths.
LAMEHUG System Data Discovery and File Assortment (Supply – Splunk)
This dynamic method ensures that the malware can adapt to completely different Home windows environments and execute contextually acceptable instructions based mostly on the AI mannequin’s understanding of system administration duties.
LAMEHUG SSH C2 Server (Supply – Splunk)
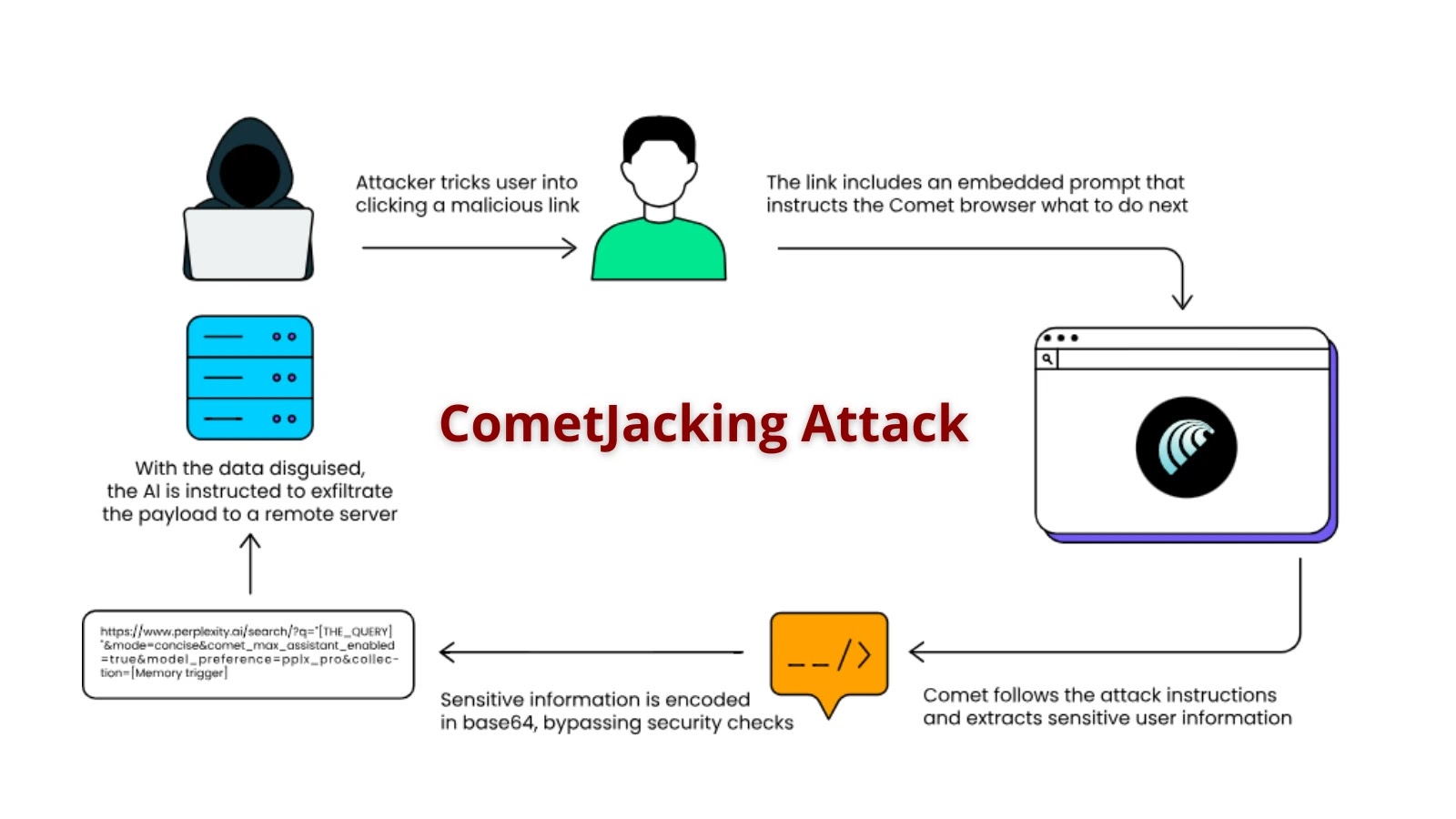
The collected data is subsequently exfiltrated by way of a number of channels, together with SSH connections to distant servers utilizing hardcoded credentials, or by way of HTTPS POST requests to command-and-control infrastructure.
Some variants encode their LLM prompts in Base64 format and make the most of completely different exfiltration endpoints, demonstrating the malware’s operational flexibility and the operators’ understanding of evasion strategies.
Comply with us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X to Get Extra Prompt Updates, Set CSN as a Most well-liked Supply in Google.