Oct 08, 2025Ravie LakshmananVulnerability / Software program Safety
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed particulars of a now-patched vulnerability within the fashionable figma-developer-mcp Mannequin Context Protocol (MCP) server that would permit attackers to attain code execution.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-53967 (CVSS rating: 7.5), is a command injection bug stemming from the unsanitized use of consumer enter, opening the door to a situation the place an attacker can ship arbitrary system instructions.
“The server constructs and executes shell instructions utilizing unvalidated consumer enter instantly inside command-line strings. This introduces the potential for shell metacharacter injection (|, >, &&, and many others.),” in response to a GitHub advisory for the flaw. “Profitable exploitation can result in distant code execution below the server course of’s privileges.”
On condition that the Framelink Figma MCP server exposes varied instruments to carry out operations in Figma utilizing synthetic intelligence (AI)-powered coding brokers like Cursor, an attacker may trick the MCP shopper to execute unintended actions by the use of an oblique immediate injection.
Cybersecurity firm Imperva, which found and reported the issue in July 2025, described CVE-2025-53967 as a “design oversight” within the fallback mechanism that would permit dangerous actors to attain full distant code execution, placing builders prone to information publicity.
The command injection flaw “happens through the development of a command-line instruction used to ship site visitors to the Figma API endpoint,” safety researcher Yohann Sillam stated.
The exploitation sequence takes place over by way of steps –
The MCP shopper sends an Initialize request to the MCP endpoint to obtain an mcp-session-id that is utilized in subsequent communication with the MCP server
The shopper sends a JSONRPC request to the MCP server with the tactic instruments/name to name instruments like get_figma_data or download_figma_images
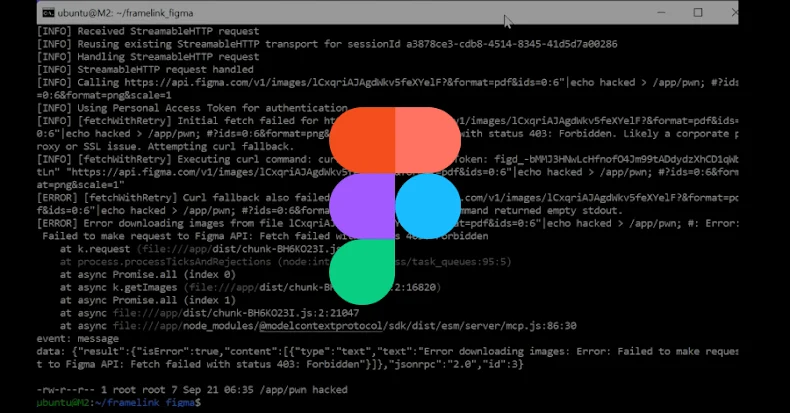
The difficulty, at its core, resides in “src/utils/fetch-with-retry.ts,” which first makes an attempt to get content material utilizing the usual fetch API and, if that fails, proceeds to executing curl command by way of child_process.exec — which introduces the command injection flaw.
“As a result of the curl command is constructed by instantly interpolating URL and header values right into a shell command string, a malicious actor may craft a specifically designed URL or header worth that injects arbitrary shell instructions,” Imperva stated. “This might result in distant code execution (RCE) on the host machine.”
In a proof-of-concept assault, a distant dangerous actor on the identical community (e.g., a public Wi-Fi or a compromised company gadget) can set off the flaw by sending the sequence of requests to the susceptible MCP. Alternatively, the attacker may trick a sufferer into visiting a specifically crafted website as a part of a DNS rebinding assault.
The vulnerability has been addressed in model 0.6.3 of figma-developer-mcp, which was launched on September 29, 2025. As mitigations, it is advisable to keep away from utilizing child_process.exec with untrusted enter and change to child_process.execFile that eliminates the chance of shell interpretation.
“As AI-driven improvement instruments proceed to evolve and acquire adoption, it is important that safety issues hold tempo with innovation,” the Thales-owned firm stated. “This vulnerability is a stark reminder that even instruments meant to run regionally can grow to be highly effective entry factors for attackers.”
The event comes as FireTail revealed that Google has opted to not repair a brand new ASCII smuggling assault in its Gemini AI chatbot that might be weaponized to craft inputs that may slip by way of safety filters and induce undesirable responses. Different giant language fashions (LLMs) vulnerable to this assault are DeepSeek and xAI’s Grok.
“And this flaw is especially harmful when LLMs, like Gemini, are deeply built-in into enterprise platforms like Google Workspace,” the corporate stated. “This system allows automated identification spoofing and systematic information poisoning, turning a UI flaw into a possible safety nightmare.”