A important vulnerability within the broadly used Sudo utility has come beneath scrutiny following the general public launch of a proof-of-concept exploit, elevating alarms for Linux system directors worldwide.
CVE-2025-32463 targets the chroot characteristic in Sudo variations 1.9.14 by 1.9.17, enabling native attackers to escalate privileges to root degree with minimal effort.
Found by safety researcher Wealthy Mirch, this flaw exploits how Sudo handles user-specified root directories, doubtlessly permitting unauthorized command execution because the superuser.
The difficulty, rated at a CVSS rating of 9.3, important, underscores ongoing dangers in privilege administration instruments important to Unix-like working programs.
Studies point out lively exploitation within the wild, prompting pressing requires patching from organizations like CISA.
This growth arrives amid a surge in Sudo-related vulnerabilities, highlighting the device’s persistent function as a chief goal for attackers in search of deeper system entry.
The vulnerability stems from Sudo’s improper decision of paths when utilizing the –chroot choice, launched in model 1.9.14 to assist user-defined root environments.
In affected variations, an attacker can craft a malicious /and so forth/nsswitch.conf file inside a managed listing, tricking Sudo into loading an arbitrary shared library throughout command analysis.
This bypasses sudoers file restrictions, granting root privileges even to customers not explicitly approved for escalation.
Wealthy Mirch recognized the problem by evaluation of Sudo’s path decision logic, noting that the chroot characteristic’s implementation creates an error-prone vector for native privilege escalation.
The flaw doesn’t require community entry or excessive privileges, making it significantly harmful in multi-user environments like servers and growth machines.
Stratascale’s advisory particulars how this might result in full system compromise, together with information exfiltration or malware deployment.
Ubuntu and Pink Hat have confirmed the vulnerability impacts their distributions, with patches rolled out in current updates.
Proof Of Idea Demonstration
The GitHub repository by researcher kh4sh3i gives a simple PoC exploit, demonstrating the escalation in a managed setting.
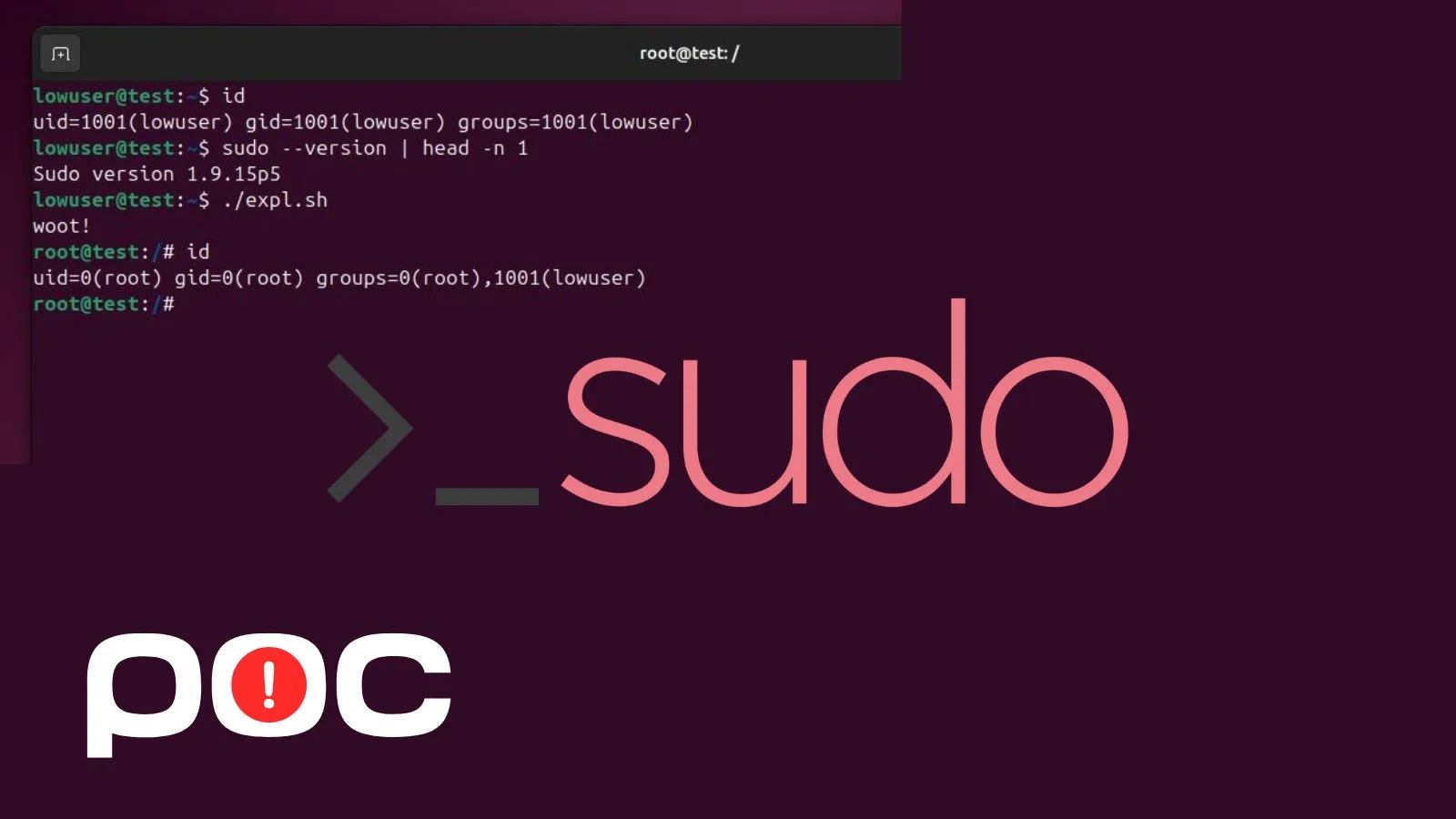
Customers clone the repository, navigate to the listing, and make the exploit.sh script executable, and run it after checking their preliminary consumer ID.
The script leverages the chroot choice to control Sudo’s surroundings, leading to a profitable privilege acquire as evidenced by the post-execution ID output exhibiting root entry.
Terminal screenshots within the repo illustrate the method: beginning as a low-privilege consumer within the lowuser group, the exploit executes by way of sudo, flipping the context to root@check with full administrative capabilities.
PoC Exploit
This visible proof, mirroring the hooked up demonstration picture, confirms the vulnerability’s reliability on unpatched programs.
Whereas meant for academic use, the PoC emphasizes the necessity for warning, as unauthorized deployment constitutes criminality. Exploit-DB hosts an analogous script, underscoring the benefit of adaptation for malicious functions.
Methods operating weak Sudo variations face extreme dangers, together with full takeover by native risk actors, which might facilitate lateral motion in breached networks.
Affected merchandise span main Linux distributions: Ubuntu 24.04 LTS, 24.10, and 25.04; Pink Hat Enterprise Linux variants; and Debian-based setups with Sudo 1.9.14-1.9.17.
Legacy variations earlier than 1.9.14 stay unaffected because of the absence of chroot assist. Quick mitigation entails updating to Sudo 1.9.17p1 or later, the place the characteristic is deprecated and the trail decision flaw is reverted.
Directors ought to allow AppArmor or SELinux profiles to constrain Sudo operations and monitor logs for suspicious chroot invocations.
CISA has added this CVE to its Recognized Exploited Vulnerabilities catalog, mandating federal businesses to use patches by October 2025.
AspectDetailsCVE IDCVE-2025-32463CVSS v3.1 Score9.3 (Essential)Assault VectorLocalImpactHigh Confidentiality, Integrity, AvailabilityAffected VersionsSudo 1.9.14 – 1.9.17Patched Versions1.9.17p1+
Organizations delaying updates threat heightened publicity, particularly in cloud and containerized environments reliant on Sudo for automation.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X for each day cybersecurity updates. Contact us to characteristic your tales.