Oct 21, 2025Ravie LakshmananMalware / Vulnerability
Cybersecurity researchers have make clear the internal workings of a botnet malware known as PolarEdge.
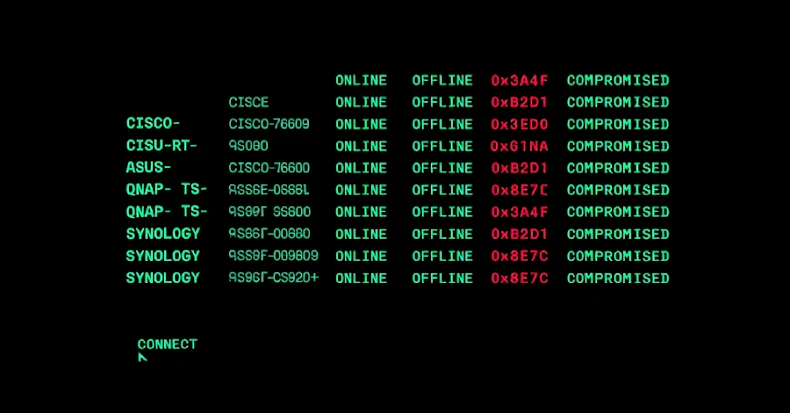
PolarEdge was first documented by Sekoia in February 2025, attributing it to a marketing campaign focusing on routers from Cisco, ASUS, QNAP, and Synology with the objective of corralling them right into a community for an as-yet-undetermined objective.
The TLS-based ELF implant, at its core, is designed to watch incoming shopper connections and execute instructions inside them.
Then, in August 2025, assault floor administration platform Censys detailed the infrastructural spine powering the botnet, with the corporate noting that PolarEdge displays traits which can be per an Operational Relay Field (ORB) community. There’s proof to recommend that the exercise involving the malware could have began way back to June 2023.
Within the assault chains noticed in February 2025, the risk actors have been noticed exploiting a recognized safety flaw impacting Cisco routers (CVE-2023-20118) to obtain a shell script named “q” over FTP, which is then liable for retrieving and executing the PolarEdge backdoor on the compromised system.
“The backdoor’s main operate is to ship a number fingerprint to its command-and-control server after which pay attention for instructions over a built-in TLS server carried out with mbedTLS,” the French cybersecurity firm mentioned in a technical breakdown of the malware.
PolarEdge is designed to assist two modes of operation: a connect-back mode, the place the backdoor acts as a TLS shopper to obtain a file from a distant server, and debug mode, the place the backdoor enters into an interactive mode to change its configuration (i.e., server info) on-the-fly.
The configuration is embedded within the ultimate 512 bytes of the ELF picture, obfuscated by a one-byte XOR that may be decrypted with single-byte key 0x11.
Nevertheless, its default mode is to operate as a TLS server in an effort to ship a number fingerprint to the command-and-control (C2) server and await instructions to be despatched. The TLS server is carried out with mbedTLS v2.8.0 and depends on a customized binary protocol for parsing incoming requests matching particular standards, together with a parameter named “HasCommand.”
Encryption algorithms used to obfuscate components of the backdoor
If the “HasCommand” parameter equals the ASCII character 1, the backdoor proceeds to extract and run the command specified within the “Command” area and transmits again the uncooked output of the executed command.
As soon as launched, PolarEdge additionally strikes (e.g., /usr/bin/wget, /sbin/curl) and deletes sure recordsdata (“/share/CACHEDEV1_DATA/.qpkg/CMS-WS/cgi-bin/library.cgi.bak”) on the contaminated gadget, though the precise objective behind this step is unclear.
Moreover, the backdoor incorporates a variety of anti-analysis methods to obfuscate info associated to the TLS server setup and fingerprinting logic. To evade detection, it employs course of masquerading throughout its initialization section by selecting from a predefined checklist a reputation at random. A number of the names included are: igmpproxy, wscd, /sbin/dhcpd, httpd, upnpd, and iapp.
“Though the backdoor doesn’t guarantee persistence throughout reboots, it calls fork to spawn a baby course of that, each 30 seconds, checks whether or not /proc/ nonetheless exists,” Sekoia researchers defined. “If the listing has disappeared, the kid executes a shell command to relaunch the backdoor.”
The disclosure comes as Synthient highlighted GhostSocks’ potential to transform compromised gadgets into SOCKS5 residential proxies. GhostSocks is alleged to have been first marketed underneath the malware-as-a-service (MaaS) mannequin on the XSS discussion board in October 2023.
It is price noting that the providing has been built-in into Lumma Stealer as of early 2024, permitting prospects of the stealer malware to monetize the compromised gadgets post-infection.
“GhostSocks supplies shoppers with the flexibility to construct a 32-bit DLL or executable,” Synthient mentioned in a current evaluation. “GhostSocks will try to find a configuration file in %TEMP%. Within the situation that the configuration file can’t be discovered, it can fall again to a hard-coded config.”
The configuration comprises particulars of the C2 server to which a connection is established for provisioning the SOCKS5 proxy and finally spawning a connection utilizing the open-source go-socks5 and yamux libraries.