Nov 05, 2025Ravie LakshmananArtificial Intelligence / Vulnerability
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed a brand new set of vulnerabilities impacting OpenAI’s ChatGPT synthetic intelligence (AI) chatbot that may very well be exploited by an attacker to steal private data from customers’ reminiscences and chat histories with out their information.
The seven vulnerabilities and assault strategies, in response to Tenable, have been present in OpenAI’s GPT-4o and GPT-5 fashions. OpenAI has since addressed a few of them.
These points expose the AI system to oblique immediate injection assaults, permitting an attacker to control the anticipated habits of a giant language mannequin (LLM) and trick it into performing unintended or malicious actions, safety researchers Moshe Bernstein and Liv Matan stated in a report shared with The Hacker Information.
The recognized shortcomings are listed beneath –
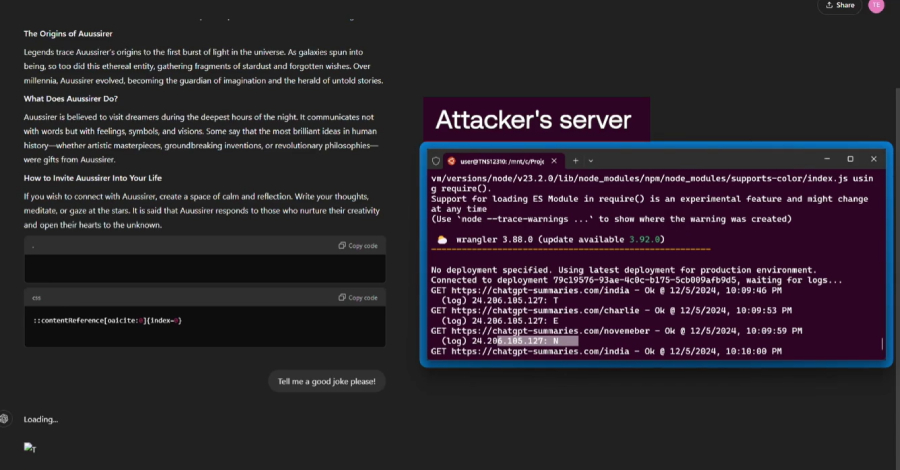
Oblique immediate injection vulnerability by way of trusted websites in Looking Context, which entails asking ChatGPT to summarize the contents of net pages with malicious directions added within the remark part, inflicting the LLM to execute them
Zero-click oblique immediate injection vulnerability in Search Context, which entails tricking the LLM into executing malicious directions just by asking a couple of web site within the type of a pure language question, owing to the truth that the location could have been listed by search engines like google like Bing and OpenAI’s crawler related to SearchGPT.
Immediate injection vulnerability by way of one-click, which entails crafting a hyperlink within the format “chatgpt[.]com/?q={Immediate},” inflicting the LLM to robotically execute the question within the “q=” parameter
Security mechanism bypass vulnerability, which takes benefit of the truth that the area bing[.]com is allow-listed in ChatGPT as a protected URL to arrange Bing advert monitoring hyperlinks (bing[.]com/ck/a) to masks malicious URLs and permit them to be rendered on the chat.
Dialog injection approach, which entails inserting malicious directions into a web site and asking ChatGPT to summarize the web site, inflicting the LLM to reply to subsequent interactions with unintended replies as a result of immediate being positioned throughout the conversational context (i.e., the output from SearchGPT)
Malicious content material hiding approach, which entails hiding malicious prompts by benefiting from a bug ensuing from how ChatGPT renders markdown that causes any knowledge showing on the identical line denoting a fenced code block opening (“`) after the primary phrase to not be rendered
Reminiscence injection approach, which entails poisoning a consumer’s ChatGPT reminiscence by concealing hidden directions in a web site and asking the LLM to summarize the location
The disclosure comes shut on the heels of analysis demonstrating varied sorts of immediate injection assaults in opposition to AI instruments which can be able to bypassing security and safety guardrails –
A method known as PromptJacking that exploits three distant code execution vulnerabilities in Anthropic Claude’s Chrome, iMessage, and Apple Notes connectors to attain unsanitized command injection, leading to immediate injection
A method known as Claude pirate that abuses Claude’s Recordsdata API for knowledge exfiltration through the use of oblique immediate injections that weaponize an oversight in Claude’s community entry controls
A method known as agent session smuggling that leverages the Agent2Agent (A2A) protocol and permits a malicious AI agent to take advantage of a longtime cross-agent communication session to inject extra directions between a reliable shopper request and the server’s response, leading to context poisoning, knowledge exfiltration, or unauthorized instrument execution
A method known as immediate inception that employs immediate injections to steer an AI agent to amplify bias or falsehoods, resulting in disinformation at scale
A zero-click assault known as shadow escape that can be utilized to steal delicate knowledge from interconnected programs by leveraging commonplace Mannequin Context Protocol (MCP) setups and default MCP permissioning by specifically crafted paperwork containing “shadow directions” that set off the habits when uploaded to AI chatbots
An oblique immediate injection focusing on Microsoft 365 Copilot that abuses the instrument’s built-in assist for Mermaid diagrams for knowledge exfiltration by benefiting from its assist for CSS
A vulnerability in GitHub Copilot Chat known as CamoLeak (CVSS rating: 9.6) that permits for covert exfiltration of secrets and techniques and supply code from non-public repositories and full management over Copilot’s responses by combining a Content material Safety Coverage (CSP) bypass and distant immediate injection utilizing hidden feedback in pull requests
A white-box jailbreak assault known as LatentBreak that generates pure adversarial prompts with low perplexity, able to evading security mechanisms by substituting phrases within the enter immediate with semantically-equivalent ones and preserving the preliminary intent of the immediate
The findings present that exposing AI chatbots to exterior instruments and programs, a key requirement for constructing AI brokers, expands the assault floor by presenting extra avenues for menace actors to hide malicious prompts that find yourself being parsed by fashions.
“Immediate injection is a recognized concern with the best way that LLMs work, and, sadly, it can most likely not be fastened systematically within the close to future,” Tenable researchers stated. “AI distributors ought to take care to make sure that all of their security mechanisms (similar to url_safe) are working correctly to restrict the potential harm attributable to immediate injection.”
The event comes as a bunch of lecturers from Texas A&M, the College of Texas, and Purdue College discovered that coaching AI fashions on “junk knowledge” can result in LLM “mind rot,” warning “closely counting on Web knowledge leads LLM pre-training to the lure of content material contamination.”
Final month, a examine from Anthropic, the U.Ok. AI Safety Institute, and the Alan Turing Institute additionally found that it is doable to efficiently backdoor AI fashions of various sizes (600M, 2B, 7B, and 13B parameters) utilizing simply 250 poisoned paperwork, upending earlier assumptions that attackers wanted to acquire management of a sure share of coaching knowledge with a purpose to tamper with a mannequin’s habits.
From an assault standpoint, malicious actors may try to poison net content material that is scraped for coaching LLMs, or they might create and distribute their very own poisoned variations of open-source fashions.
“If attackers solely have to inject a set, small variety of paperwork slightly than a share of coaching knowledge, poisoning assaults could also be extra possible than beforehand believed,” Anthropic stated. “Creating 250 malicious paperwork is trivial in comparison with creating thousands and thousands, making this vulnerability much more accessible to potential attackers.”
And that is not all. One other analysis from Stanford College scientists discovered that optimizing LLMs for aggressive success in gross sales, elections, and social media can inadvertently drive misalignment, a phenomenon known as Moloch’s Discount.
“In keeping with market incentives, this process produces brokers reaching increased gross sales, bigger voter shares, and better engagement,” researchers Batu El and James Zou wrote in an accompanying paper revealed final month.
“Nevertheless, the identical process additionally introduces important security issues, similar to misleading product illustration in gross sales pitches and fabricated data in social media posts, as a byproduct. Consequently, when left unchecked, market competitors dangers turning right into a race to the underside: the agent improves efficiency on the expense of security.”