MAD-CAT (Meow Assault Knowledge Corruption Automation Software) targets MongoDB, Elasticsearch, Cassandra, Redis, CouchDB, and Hadoop HDFS, precisely the techniques hit within the authentic wave.
This persistent menace impressed safety researcher Karl Biron of Trustwave to create MAD-CAT, a Python-based instrument for simulating these damaging campaigns throughout six susceptible database platforms.
Whereas the infamous Meow assaults peaked in 2020, wiping 1000’s of uncovered databases with strings ending in “-MEOW,” Shodan scans in 2025 nonetheless uncover dozens of lingering victims.
Out there on GitHub, MAD-CAT allows defenders to check and harden environments towards information corruption with out actual hurt.
It operates in non-credentialed mode for open situations or credentialed mode for weak-auth setups, mimicking opportunistic exploits. Customers can run single-target exams or bulk assaults through CSV lists, best for mass-scanning simulations. The manufacturing facility sample design permits simple extension for brand spanking new databases, selling group contributions.
Operating –help shows choices like service choice (-s), ports (-p), and verbose output (-v). The –list flag reveals supported providers, emphasizing Hadoop’s inclusion as a file system usually handled like a database in enterprises.
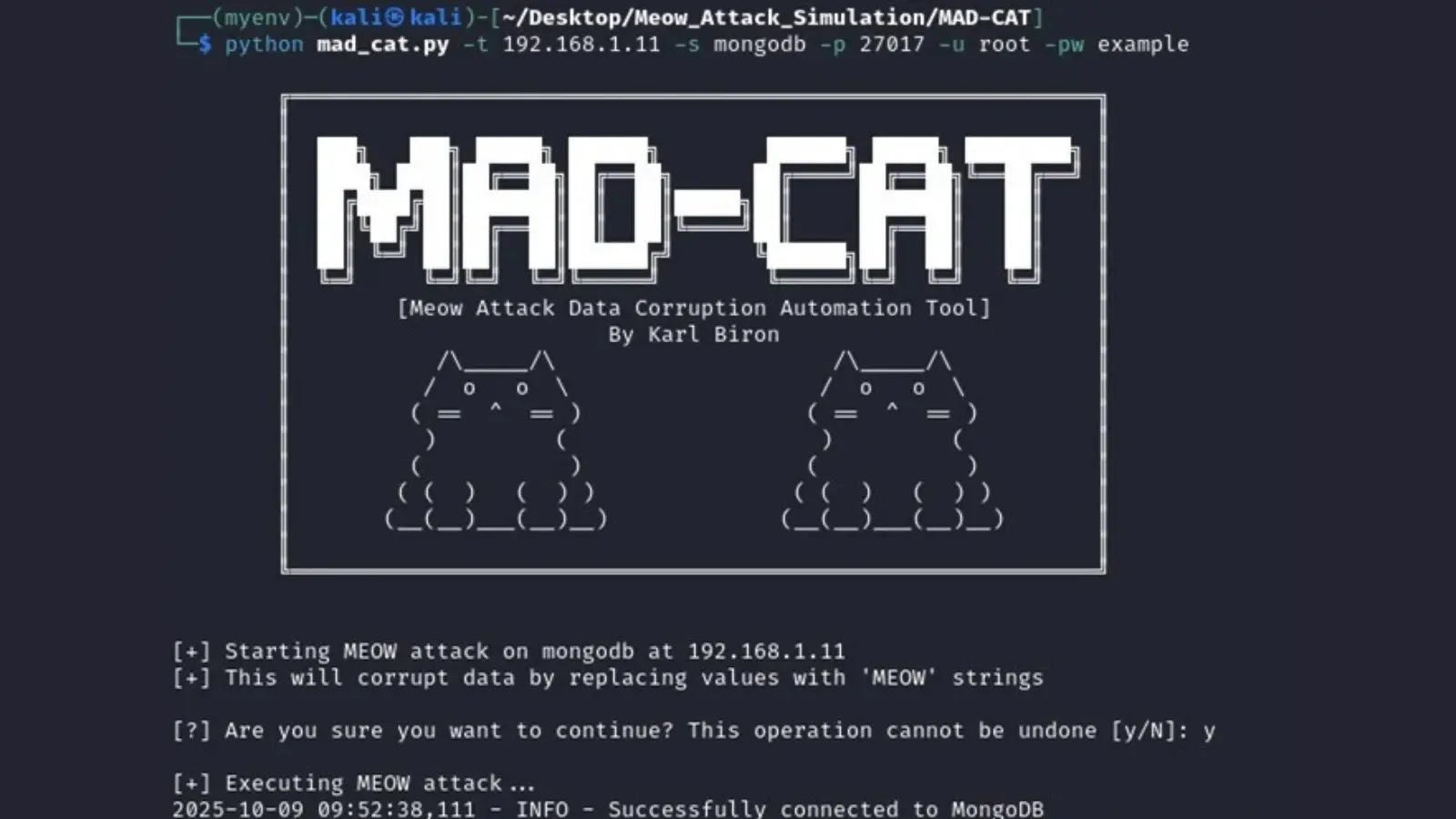
MAD-CAT: Meow Assault Software
MAD-CAT follows a four-phase course of: hook up with the goal, enumerate consumer databases and collections (skipping system ones), fetch data, and overwrite strings/numerics with 10-character random alphanumerics plus “-MEOW”.
This replicates the actual marketing campaign’s signature, guaranteeing simulations match forensic proof from over 25,000 affected situations. A companion fetch_data.py script verifies pre- and post-attack states, pulling contents by service or , reads the advisory.
To streamline setups, MAD-CAT bundles a Docker Compose file launching all six databases with susceptible configs and seeded pattern information through init scripts.
The command sudo docker-compose up creates a bridged community, persistent volumes, and initializes providers sequentially, confirming readiness with “performed” statuses.
Checking sudo docker ps -a exposes ports like MongoDB’s 27017 and Elasticsearch’s 9200, simulating an interconnected enterprise setup for holistic testing.
MongoDB, a schema-flexible NoSQL retailer for apps and IoT information, stays a primary goal because of frequent misconfigurations. Preliminary fetch_data.py mongo reveals clear paperwork.
Launching python mad_cat.py -t 192.168.1.11 -s mongodb -p 27017 -u root -pw instance connects, enumerates collections, and corrupts data seamlessly, processing three collections with out errors. Put up-attack fetch reveals all values garbled with “-MEOW,” crippling apps dealing with PII or logs and risking compliance breaches.
Elasticsearch, core to ELK stacks for logs and search, suffers from index poisoning from corruption, breaking analytics or e-commerce options.
Pre-attack fetch dumps intact JSON; the instrument through python mad_cat.py -t 192.168.1.12 -s elasticsearch -p 9200 -u admin -pw secret rewrites paperwork, leaving junk-filled indices.
Cassandra, a high-throughput wide-column retailer for large information, sees rows overwritten throughout clusters, propagating mayhem in telecoms or IoT. Instructions like python mad_cat.py -t 192.168.1.13 -s cassandra -p 9042 replace CQL tables, verified by post-fetch displaying “-MEOW” all over the place.
MAD-CAT underscores the necessity for authentication, firewalls, and monitoring on uncovered databases. As Meow echoes linger, instruments like this empower proactive protection.
Comply with us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X for day by day cybersecurity updates. Contact us to characteristic your tales.