A brand new, extremely refined malware marketing campaign has been recognized focusing on distant staff and organizations by means of a pretend Google Meet touchdown web page.
Hosted on the misleading area gogl-meet[.]com, this assault leverages the “ClickFix” social engineering approach to bypass conventional browser safety controls and ship a Distant Entry Trojan (RAT) on to the sufferer’s system.
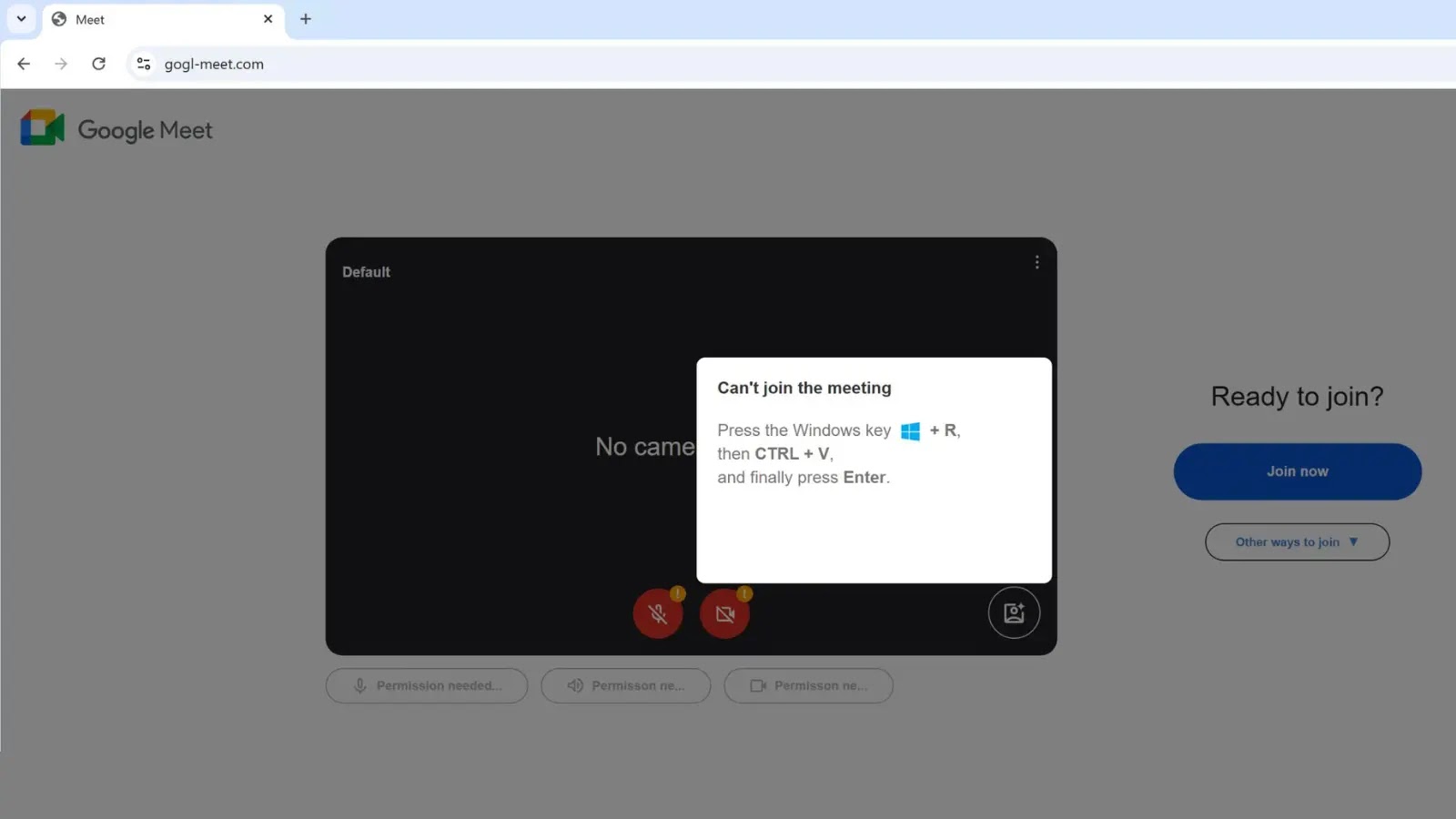
The assault begins when a person navigates to the fraudulent web site, which is visually indistinguishable from the respectable Google Meet interface. As an alternative of a video feed, the person is interrupted by a pop-up error message, sometimes claiming a digicam or microphone subject titled “Can’t be a part of the assembly.”
In contrast to commonplace phishing that asks for credentials, this web page provides a technical “repair” that requires bodily person interplay. The immediate instructs the sufferer to carry out a particular sequence of keystrokes: Press the Home windows key + R, then CTRL + V, and eventually Enter.
Unbeknownst to the person, clicking the “Be a part of now” or “Repair” button on the web page triggers a JavaScript operate that copies a malicious PowerShell script to their clipboard.
By following the guide keystroke directions, the person unwittingly pastes and executes this script by way of the Home windows Run dialog, successfully bypassing browser-based safety filters corresponding to Google Secure Looking and SmartScreen.
Forensic Evaluation and Indicators
Current incident response actions involving gogl-meet[.]com have confirmed that this chain results in a RAT an infection. Forensic evaluation of affected methods recognized the an infection’s root trigger by means of the Grasp File Desk (MFT).
Particularly, the MFT entry for the dropped payload revealed important origin knowledge in its Different Information Stream (ADS), capturing each the ClickFix downloaded file and the referrer URL gogl-meet[.]com.
This forensic artifact is essential for defenders, because it definitively hyperlinks the execution of the RAT again to the browser-based social engineering occasion moderately than a typical drive-by obtain or e mail attachment.
A definite attribute of this wave is the obfuscation used throughout the PowerShell payload itself. Risk actors have begun padding the malicious script with in depth feedback containing trusted visible symbols, corresponding to repeated inexperienced verify marks (✅).
When a person pastes the content material into the small Home windows Run field, these symbols stands out as the solely seen textual content, visually reassuring the sufferer that the command is “verified” or protected [memory].
This tactic additionally serves a technical goal: it may well push the precise malicious code (typically an IEX obtain cradle) out of the instant seen space of the dialog field, masking the script’s true intent.
Whereas ClickFix (additionally related to clusters like ClearFake) gained important traction all through 2024, this newest iteration demonstrates a shift towards hyper-targeted branding.
Early campaigns impersonated generic browser updates or Phrase errors. Nonetheless, the shift to Google Meet simulation suggests a pivot towards focusing on company environments the place video conferencing glitches are a standard, trusted friction level.
Safety groups are suggested to replace detection guidelines to flag PowerShell execution strings originating from the Run dialog that comprise uncommon Unicode characters or in depth remark blocks, that are tell-tale indicators of guide execution.
Comply with us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X for every day cybersecurity updates. Contact us to characteristic your tales.