A severe privilege escalation vulnerability in K7 Final Safety, an antivirus product from K7 Computing, was discovered by abusing named pipes with overly permissive entry management lists.
This flaw permits low-privileged customers to control registry settings and obtain SYSTEM-level entry with out triggering UAC prompts, prompting a number of patch makes an attempt that researchers bypassed.
The difficulty surfaced throughout the investigation by Safety researcher Lucas Laise from Quarkslab uncovered an unrelated denial-of-service vulnerability, CVE-2024-36424, affecting K7RKScan.sys in variations earlier than 17.0.2019.
Preliminary testing on model 17.0.2045 revealed restricted performance for non-admin customers, together with the lack to switch configurations with out elevation.
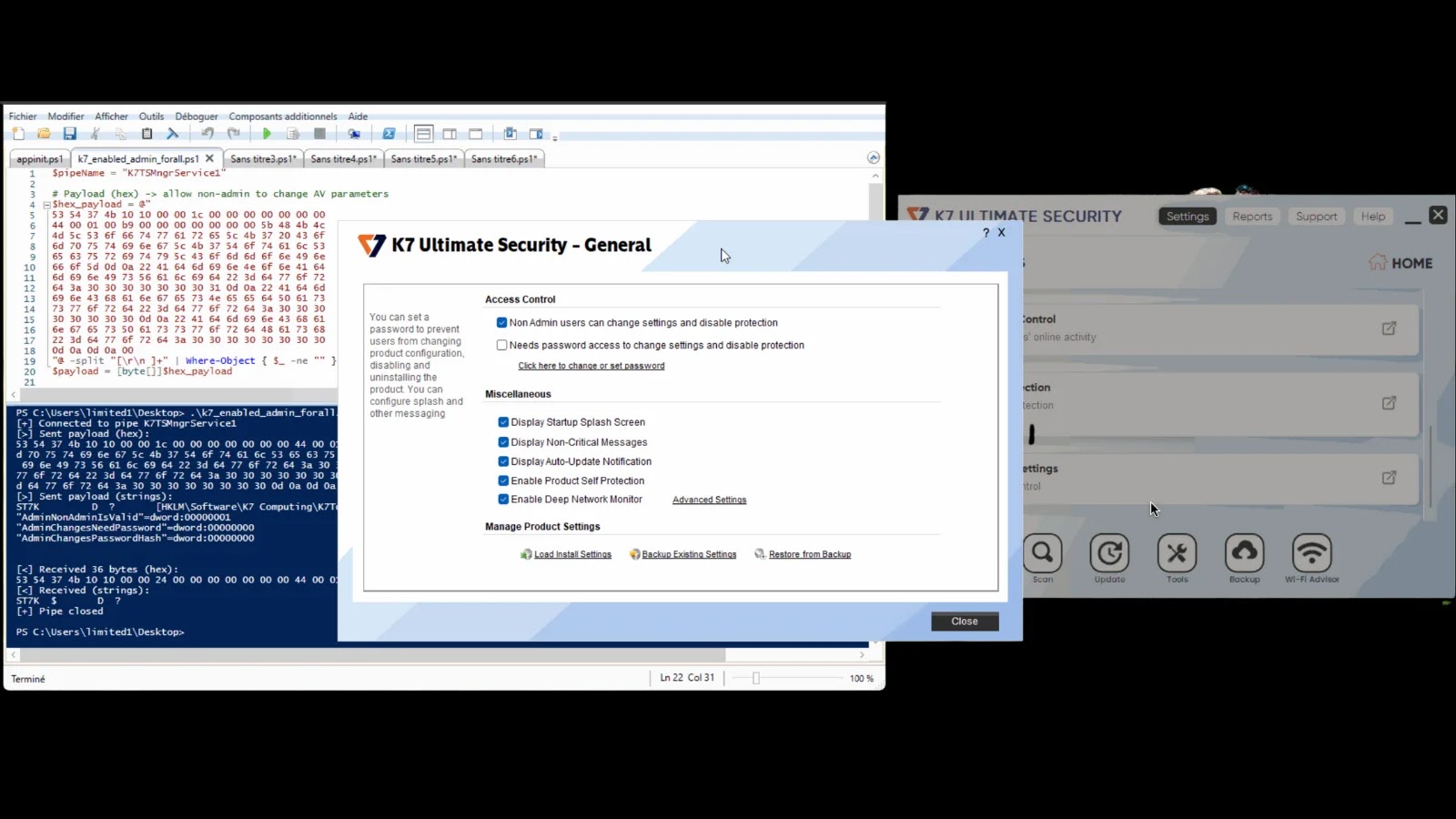
Directors might allow “non-admin customers can change settings and disable safety” with out UAC, hinting at inter-process communication flaws. Instruments like PipeViewer recognized SYSTEM-owned named pipes, together with .pipeK7MailProxyV1 with full permissions and .pipeK7TSMngrService1 utilized by K7TSMain.exe for registry modifications.
IoNinja captures confirmed binary payloads despatched to K7TSMngrService1 throughout setting modifications, with Procmon verifying SYSTEM-context execution. This communication path grew to become the exploitation vector, as low-privilege processes might impersonate reliable requests.
Attackers replay captured packets by way of PowerShell to allow common configuration tampering, disabling real-time scans or whitelisting malware.
Additional refinement focused registry key AdminNonAdminIsValid; a one-byte size manipulation (B9 to B8 hex) allowed arbitrary worth injection, evading validation.
For full native privilege escalation, researchers exploited Picture File Execution Choices (MITRE ATT&CK T1546.012) by setting a debugger on K7TSHlpr.exe to execute arbitrary code as SYSTEM throughout pretend updates. A supplied script creates a batch file for brand new admin customers, triggers the replace, and cleans up.
K7 issued three patches: first added caller validation on K7TSMngrService1, bypassed by way of handbook DLL mapping into k7tsmngr.exe. The second, by way of K7Sentry.sys driver model 22.0.0.70, blocked injection into protected processes, circumvented utilizing renamed signed K7 binaries like K7QuervarCleaningTool.exe outdoors protected lists.
Root-cause evaluation in IDA Professional revealed that ValidatePipeClient checks for the set up path, MD5 hashes, and K7 signatures, plus K7Sentry’s VDefProtectedProcs registry whitelist. Bypasses relied on unsigned or relocated signed binaries, evading each pipe entry and safety hooks.
Accountable disclosure spanned August to December 2025, with Quarkslab notifying K7 on August 25 and publishing on December 2 after bypass confirmations. K7 deferred full ACL enforcement to a future main launch, acknowledging interim fixes.
Customers ought to replace to the newest variations and monitor for complete remediation. Exploit scripts can be found on the Quarkslab weblog for defensive evaluation.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X for every day cybersecurity updates. Contact us to characteristic your tales.