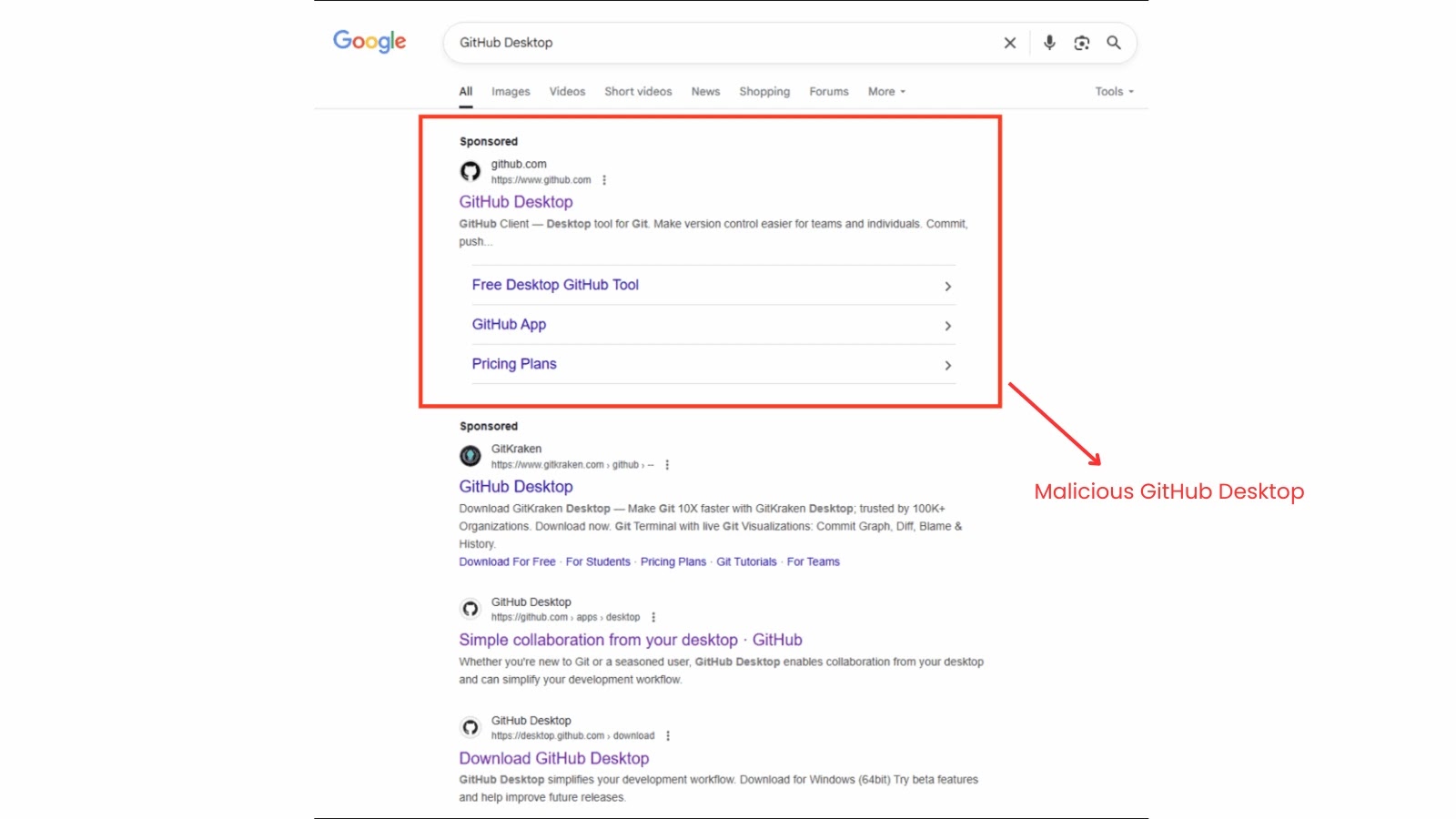
In as we speak’s digital world, databases act as fortified storehouses for a company’s crown jewels its essential knowledge. But these vaults face nonstop assaults from cyber threats.
As a cybersecurity defender, you stand because the ever-watchful guardian, shielding these belongings from relentless foes. Success calls for a strategic blueprint for each database underneath your purview.
This information charts the trail by way of database safety’s challenges, outlining 10 confirmed greatest practices to lock down your methods and thwart attackers.
1. Information Classification
Information classification is the foundational step in database safety. It includes categorizing your knowledge based mostly on its significance and sensitivity, which you’ll later safeguard with database software program applications and measures designed to extend safety.
Prioritize safety efforts, guaranteeing that probably the most delicate knowledge receives the best degree of safety.
To successfully implement knowledge classification, comply with these steps:
Stock Your Information: Determine all knowledge belongings inside your group. This contains knowledge saved in databases, file servers, cloud storage, and bodily paperwork. You possibly can’t shield what you don’t know exists.
Outline Information Classes: Create a classification scheme that fits your group’s wants. Frequent classes embody “public,” “inside use solely,” “confidential,” and “restricted.” Be sure that these classes align with your online business targets and compliance necessities.
Assign Accountability: Designate people or groups liable for knowledge classification. They need to be well-versed within the group’s knowledge, worth, and potential dangers.
Implement Classification Instruments: Spend money on instruments and applied sciences that facilitate knowledge classification. Automated options can scan and tag knowledge based mostly on predefined standards, making the method extra environment friendly and constant.
Educate Workers: Practice your workers on knowledge classification rules and their position in safeguarding delicate knowledge. Ensure that they perceive the significance of adequately labeling and dealing with labeled info.
Assessment and Revise: Recurrently replace your knowledge classification scheme to adapt to altering enterprise wants and threats. Information classification will not be a static course of; it ought to evolve together with your group.
2. Encryption
Encryption is like placing your knowledge in a safe vault with a lock solely you possibly can open. Once you encrypt knowledge, it transforms into an unreadable format with out the encryption key. Encryption ensures that even when an unauthorized occasion positive aspects entry to the information, it stays indecipherable with out the proper decryption key.
Listed here are some greatest practices for implementing encryption:
Use Robust Algorithms: Depend on well-established encryption algorithms like AES-256 for sturdy safety towards trendy cyber threats.
Safe Key Administration: Correctly handle encryption keys, guaranteeing their era, storage, and rotation are dealt with securely. Unauthorized entry to encryption keys can compromise your entire system.
Restrict Entry: Implement stringent entry controls to make sure solely approved people can entry encryption keys and encrypted knowledge.
Common Updates: Keep up to date with the newest encryption requirements and practices. Vulnerabilities will be found over time, and patches are important for sustaining the effectiveness of your encryption technique.
Complete Technique: Mix encryption with safety measures like entry controls, auditing, and intrusion detection to create a layered protection towards potential threats.
3. Robust Authentication
Authentication is your first line of protection towards unauthorized entry. Implement robust password insurance policies that require customers to create complicated passwords. Strive utilizing passphrase-based authentication for added safety.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) goes a step additional by insisting on customers offering two or extra verification kinds, similar to a password and a fingerprint scan or a code from a cellular app. It considerably reduces the chance of unauthorized entry by including this additional layer of verification.
Passwords will be stolen by way of methods like phishing or keylogging. Robust authentication, particularly MFA, mitigates the impression of stolen credentials as a result of even when an attacker has the password, they received’t have the second issue required for entry.
For directors or customers with elevated privileges, robust authentication is paramount. Unauthorized modifications to the database configuration or knowledge can have catastrophic penalties. Robust authentication ensures that solely approved people could make modifications.
Many regulatory frameworks and business requirements, similar to PCI DSS and HIPAA, mandate robust authentication practices for knowledge safety. Compliance will not be non-obligatory, and powerful authentication is a elementary requirement.
4. Common Patching and Updates
Database software program will not be resistant to vulnerabilities. Recurrently apply patches and updates the database vendor offers to maintain your database safe. Cybercriminals usually exploit identified vulnerabilities in unpatched methods, making this a essential observe to stop safety breaches.
Listed here are a number of recommendations on what you are able to do:
Set up a Patch Administration Coverage: Develop a transparent and documented patch administration coverage that outlines roles and duties, testing patches’ procedures, and a deployment timeline.
Patch Testing: Earlier than making use of patches in a manufacturing surroundings, check them in a managed and non-critical surroundings. This helps establish potential conflicts or points arising from the patch.
Prioritize Vital Patches: Prioritize putting in essential patches to guard your most delicate knowledge.
Recurrently Monitor for Updates: Keep knowledgeable about patch releases and updates out of your database vendor. Subscribe to safety mailing lists or notifications for well timed details about vulnerabilities and obtainable patches.
Automate Patching: Think about implementing automated patch administration instruments to streamline the method, guaranteeing that patches are utilized constantly and promptly.
Backup Earlier than Patching: This ensures that within the uncommon occasion {that a} patch causes sudden points, you possibly can shortly restore your system to a identified good state.
Schedule Downtime Properly: Plan patching and updates throughout upkeep home windows or occasions of decrease person exercise to reduce disruption to your group’s operations.
Audit and Verification: After making use of patches, conduct audits to confirm that the patches had been efficiently utilized and that the database capabilities as anticipated.
Documentation: Preserve detailed information of patching and replace actions—doc which patches had been utilized, when, and any points encountered.
5. Entry Management
Entry management is about who will get in and what they will do as soon as they’re inside. It defines and enforces insurance policies figuring out who can entry your database, what they will do as soon as inside, and underneath what circumstances.
Implement role-based entry management (RBAC) to handle person permissions effectively. Outline roles and assign particular privileges to every place based mostly on job duties. This minimizes the complexity of safety administration, decreasing the probability of misconfigurations that might result in safety vulnerabilities.
Meticulously defining entry rights and privileges permits you to be sure that solely approved customers or methods are granted entry to delicate info.
Keep away from giving customers extra entry than they want; the precept of least privilege ensures that customers solely have the permissions essential to carry out their duties. Recurrently evaluate and modify entry rights as roles evolve inside your group.
6. Audit and Monitoring
Consider auditing and monitoring as your database’s watchful guardian. These practices present a proactive and reactive method to database safety, providing a number of layers of safety.
Auditing and monitoring present a retrospective view of database actions, which is invaluable for investigations, compliance, and forensic evaluation. Audit logs seize an in depth document of all actions, together with logins, knowledge modifications, and configuration modifications.
Allow auditing options to document all person actions inside the database. Recurrently evaluate these logs to detect uncommon or unauthorized actions, similar to a number of login makes an attempt, knowledge modifications, or configuration modifications.
Implement real-time monitoring to obtain alerts for suspicious actions, enabling fast response to potential threats. Actual-time monitoring may help establish and handle efficiency points or system glitches earlier than they impression the person expertise or disrupt operations, guaranteeing clean database operation.
Moreover, audit logs are essential for compliance with knowledge safety laws and business requirements, similar to GDPR or HIPAA, as they supply proof of adherence to safety insurance policies and practices.
In essence, audit and monitoring are the silent sentinels that not solely proactively guard your database towards threats but in addition present essential insights and proof for retrospective evaluation and compliance assurance.
7. Backup and Restoration
Information loss can happen for numerous causes, together with cyberattacks, {hardware} failures, or human error. Recurrently again up your database and check your backup and restoration procedures to make sure knowledge integrity. Doc a transparent restoration plan with step-by-step directions for restoration.
Frequent backups and a well-practiced restoration plan are your lifelines in an information catastrophe, serving to decrease downtime and knowledge loss.
Implementing greatest practices in backup and restoration includes a number of key issues:
Frequency and Retention: Decide the frequency of backups (e.g., each day, hourly) based mostly in your knowledge’s criticality and the speed of change. Set up retention insurance policies that specify how lengthy backups are saved.
Backup Testing: Recurrently check your backup and restoration procedures to make sure they work as anticipated. This helps establish and rectify points earlier than they develop into essential.
Offsite and Redundant Storage: Retailer backup copies in safe, offsite places or on redundant methods to guard towards bodily disasters which will have an effect on the first knowledge heart.
Encryption: Encrypt backup knowledge to guard it from unauthorized entry, guaranteeing that delicate info stays safe even in backup copies.
Documentation: Keep thorough documentation of your backup and restoration processes, together with procedures, schedules, and get in touch with info for key personnel liable for restoration.
Automated Backup Options: Think about implementing automated backup options that streamline the method, scale back the chance of human error, and guarantee backups are constantly carried out.
8. Safe Configuration
Securing database configurations is a essential greatest observe for enhancing database security. It includes the meticulous design of your database administration system to reduce safety dangers.
Adhering to safe configuration pointers reduces the assault floor and vulnerabilities, making it tougher for cybercriminals to use weaknesses.
Database methods include default settings that might not be optimized for safety. Seek the advice of your database vendor’s safety pointers and greatest practices to configure your database securely. Disable pointless options and companies that attackers might exploit. Adhere to the precept of least privilege to make use of entry to maintain databases protected.
Recurrently evaluate and replace your configuration to align with the newest safety suggestions. It’s a proactive method to database safety that helps fortify your defenses towards potential threats, guaranteeing your database operates in a hardened and resilient state.
9. Intrusion Detection and Prevention
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Methods (IDPS) are just like safety guards to your database. They’re very important greatest practices for bolstering database safety. They act as real-time sentinels, monitoring community site visitors and system actions for indicators of malicious or unauthorized habits.
They repeatedly monitor community site visitors and system actions, looking for patterns that point out potential threats. They will generate alerts or take automated actions to dam or mitigate assaults.
Implementing IDPS is essential within the trendy risk panorama, the place persistent cyberattacks are evolving.
Intrusion detection identifies potential threats, whereas intrusion prevention instantly blocks or mitigates assaults. These measures are essential the place cyberattacks are persistent and evolving.
Implementing intrusion detection and prevention methods permits you to swiftly detect and reply to safety breaches, decreasing the chance of information compromise and guaranteeing the continued integrity of your database.
10. Worker Coaching
Workers are sometimes the weakest hyperlink in cybersecurity. Complete safety consciousness coaching is important. Train your group easy methods to acknowledge phishing makes an attempt, social engineering techniques, and the significance of safe password administration.
Common coaching periods and simulated workout routines assist workers perceive their position in sustaining database safety. An knowledgeable and vigilant workforce considerably reduces the chance of safety breaches attributable to human error.
To maximise the effectiveness of worker coaching:
Recurrently Replace Content material: Cyber threats evolve, so coaching content material needs to be up to date periodically to handle new dangers and methods attackers use.
Simulated Workouts: Conduct simulated workout routines like phishing drills to check workers’ potential to acknowledge and reply to threats.
Engagement and Suggestions: Make coaching participating and interactive, permitting workers to ask questions and search clarification.
Steady Studying: Encourage workers to remain knowledgeable about cybersecurity developments by offering entry to related sources and inspiring them to attend workshops or webinars.
Remaining Ideas
In conclusion, these ten greatest practices kind the spine of a sturdy database safety technique. They require ongoing consideration and dedication to adapt to the ever-changing cybersecurity panorama.
Implementing these practices diligently permits you to fortify your group’s database safety and contribute to its total resilience towards cyber threats.