The just lately found refined Linux malware framework referred to as VoidLink is assessed to have been developed by a single individual with help from a synthetic intelligence (AI) mannequin.
That is based on new findings from Test Level Analysis, which recognized operational safety blunders by malware’s creator that offered clues to its developmental origins. The most recent perception makes VoidLink one of many first cases of a complicated malware largely generated utilizing AI.
“These supplies present clear proof that the malware was produced predominantly by means of AI-driven growth, reaching a primary purposeful implant in below per week,” the cybersecurity firm mentioned, including it reached greater than 88,000 strains of code by early December 2025.
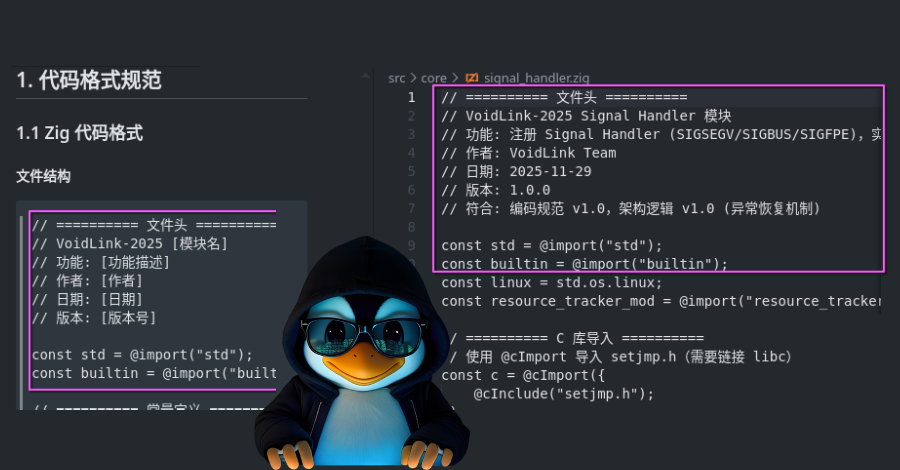
VoidLink, first publicly documented final week, is a feature-rich malware framework written in Zig that is particularly designed for long-term, stealthy entry to Linux-based cloud environments. The malware is alleged to have come from a Chinese language-affiliated growth surroundings. As of writing, the precise function of the malware stays unclear. No real-world infections have been noticed so far.
A follow-up evaluation from Sysdig was the primary to spotlight the truth that the toolkit might have been developed with the assistance of a giant language mannequin (LLM) below the instructions of a human with intensive kernel growth data and crimson workforce expertise, citing 4 completely different items of proof –
Overly systematic debug output with completely constant formatting throughout all modules
Placeholder knowledge (“John Doe”) is typical of LLM coaching examples embedded in decoy response templates
Uniform API versioning the place all the things is _v3 (e.g., BeaconAPI_v3, docker_escape_v3, timestomp_v3)
Template-like JSON responses masking each doable discipline
“The most certainly situation: a talented Chinese language-speaking developer used AI to speed up growth (producing boilerplate, debug logging, JSON templates) whereas offering the safety experience and structure themselves,” the cloud safety vendor famous late final week.
Test Level’s Tuesday report backs up this speculation, stating it recognized artifacts suggesting that the event in itself was engineered utilizing an AI mannequin, which was then used to construct, execute, and take a look at the framework – successfully turning what was an idea right into a working instrument inside an accelerated timeline.
Excessive-level overview of the VoidLink Challenge
“The final method to creating VoidLink might be described as Spec Pushed Growth (SDD),” it famous. “On this workflow, a developer begins by specifying what they’re constructing, then creates a plan, breaks that plan into duties, and solely then permits an agent to implement it.”
It is believed that the risk actor commenced work on the VoidLink in late November 2025, leveraging a coding agent referred to as TRAE SOLO to hold out the duties. This evaluation relies on the presence of TRAE-generated helper information which were copied together with the supply code to the risk actor’s server and later leaked in an uncovered open listing.
As well as, Test Level mentioned it uncovered inside planning materials written in Chinese language associated to dash schedules, characteristic breakdowns, and coding pointers which have all of the hallmarks of LLM-generated content material — well-structured, constantly formatted, and meticulously detailed. One such doc detailing the event plan was created on November 27, 2025.
The documentation is alleged to have been repurposed as an execution blueprint for the LLM to observe, construct, and take a look at the malware. Test Level, which replicated the implementation workflow utilizing the TRAE IDE utilized by the developer, discovered that the mannequin generated code that resembled VoidLink’s supply code.
Translated growth plan for 3 groups: Core, Arsenal, and Backend
“A evaluation of the code standardization directions in opposition to the recovered VoidLink supply code reveals a hanging stage of alignment,” it mentioned. “Conventions, construction, and implementation patterns match so intently that it leaves little room for doubt: the codebase was written to these precise directions.”
The event is one more signal that, whereas AI and LLMs might not equip dangerous actors with novel capabilities, they will additional decrease barrier of entry to malicious actors, empowering even a single particular person to examine, create, and iterate complicated methods rapidly and pull off refined assaults — streamlining what was as soon as a course of that required a big quantity of effort and assets and out there solely to nation-state adversaries.
“VoidLink represents an actual shift in how superior malware might be created. What stood out wasn’t simply the sophistication of the framework, however the velocity at which it was constructed,” Eli Smadja, group supervisor at Test Level Analysis, mentioned in a press release shared with The Hacker Information.
“AI enabled what seems to be a single actor to plan, develop, and iterate a posh malware platform in days – one thing that beforehand required coordinated groups and vital assets. This can be a clear sign that AI is altering the economics and scale of cyber threats.”
In a whitepaper revealed this week, Group-IB described AI as supercharging a “fifth wave” within the evolution of cybercrime, providing ready-made instruments to allow refined assaults. “Adversaries are industrialising AI, turning as soon as specialist abilities resembling persuasion, impersonation, and malware growth into on-demand providers out there to anybody with a bank card,” it mentioned.
The Singapore-headquartered cybersecurity firm famous that darkish internet discussion board posts that includes AI key phrases have seen a 371% enhance since 2019, with risk actors promoting darkish LLMs like Nytheon AI that shouldn’t have any moral restrictions, jailbreak frameworks, and artificial id kits providing AI video actors, cloned voices, and even biometric datasets for as little as $5.
“AI has industrialized cybercrime. What as soon as required expert operators and time can now be purchased, automated, and scaled globally,” Craig Jones, former INTERPOL director of cybercrime and unbiased strategic advisor, mentioned.
“Whereas AI hasn’t created new motives for cybercriminals — cash, leverage, and entry nonetheless drive the ecosystem – it has dramatically elevated the velocity, scale, and class with which these motives are pursued.”