Microsoft has warned of a multi‑stage adversary‑in‑the‑center (AitM) phishing and enterprise electronic mail compromise (BEC) marketing campaign concentrating on a number of organizations within the vitality sector.
“The marketing campaign abused SharePoint file‑sharing providers to ship phishing payloads and relied on inbox rule creation to take care of persistence and evade person consciousness,” the Microsoft Defender Safety Analysis Workforce mentioned. “The assault transitioned right into a collection of AitM assaults and follow-on BEC exercise spanning a number of organizations.”
As a part of post-exploitation exercise following preliminary compromise, the unknown attackers have been discovered to leverage trusted inner identities from the sufferer to hold out giant‑scale intra‑organizational and exterior phishing in an effort to solid a large web and widen the scope of the marketing campaign.
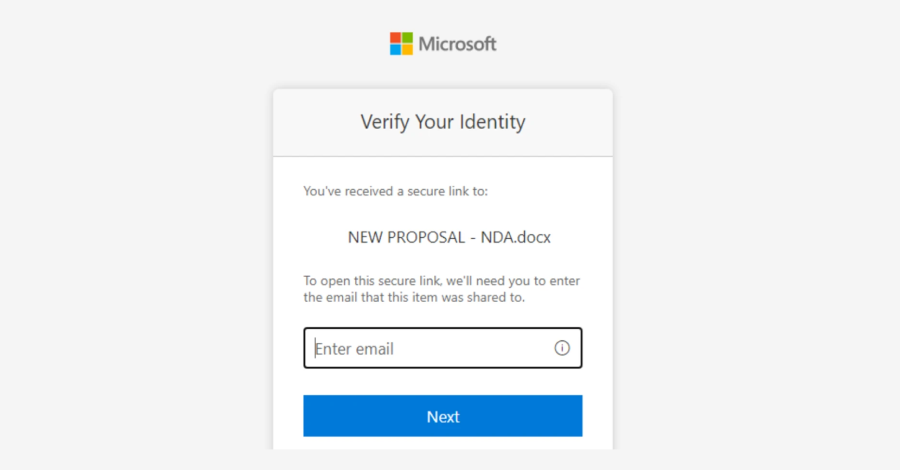
The place to begin of the assault is a phishing electronic mail doubtless despatched from an electronic mail tackle belonging to a trusted group, which was compromised beforehand. Abusing this respectable channel, the risk actors despatched out messages masquerading as SharePoint doc‑sharing workflows to offer it a veneer of credibility and trick recipients into clicking on phishing URLs.
As a result of providers like SharePoint and OneDrive are extensively utilized in enterprise environments and the emails originate from a respectable tackle, they’re unlikely to boost suspicion, permitting adversaries to ship phishing hyperlinks or stage malicious payloads. This method can be referred to as living-off-trusted-sites (LOTS), because it weaponizes the familiarity and ubiquity of such platforms to subvert electronic mail‑centric detection mechanisms.
The URL, for its half, redirects customers to a pretend credential immediate to view the purported doc. Armed with entry to the account utilizing the stolen credentials and the session cookie, the attackers create inbox guidelines to delete all incoming emails and mark all emails as learn. With this basis in place, the compromised inbox is used to ship phishing messages containing a pretend URL designed to conduct credential theft utilizing an AitM assault.
In a single case, Microsoft mentioned the attacker initiated a large-scale phishing marketing campaign involving greater than 600 emails that have been despatched to the compromised person’s contacts, each inside and out of doors of the group. The risk actors have additionally been noticed taking steps to delete undelivered and out of workplace emails, and guarantee message recipients of the e-mail’s authenticity in the event that they raised any issues. The correspondence is then deleted from the mailbox.
“These methods are widespread in any BEC assaults and are supposed to maintain the sufferer unaware of the attacker’s operations, thus serving to in persistence,” the Home windows maker famous.
Microsoft mentioned the assault highlights the “operational complexity” of AitM, stating password resets alone can’t remediate the risk, as impacted organizations should make sure that they’ve revoked energetic session cookies and eliminated attacker-created inbox guidelines used to evade detection.
To that finish, the corporate famous that it labored with clients to revoke multi-factor authentication (MFA) modifications made by the attacker on the compromised person’s accounts and delete suspicious guidelines created on these accounts. It is at present not recognized what number of organizations have been compromised and if it is the work of any recognized cybercrime group.
Organizations are suggested to work with their id supplier to verify safety controls like phishing-resistant MFA are in place, allow conditional entry insurance policies, implement steady entry analysis, and use anti-phishing options that monitor and scan incoming emails and visited web sites.
The assault outlined by Microsoft highlights the continued pattern amongst risk actors to abuse trusted providers resembling Google Drive, Amazon Net Providers (AWS), and Atlassian’s Confluence wiki to redirect to credential harvesting websites and stage malware. This eliminates the necessity for attackers to construct out their very own infrastructure in addition to makes malicious exercise seem respectable.
The disclosure comes as id providers supplier Okta mentioned it detected customized phishing kits which might be designed particularly to be used in voice phishing (aka vishing) campaigns concentrating on Google, Microsoft, Okta, and a variety of cryptocurrency platforms. In these campaigns, the adversary, posing as tech help personnel, calls potential targets utilizing a spoofed help hotline or firm telephone quantity.
The assaults goal to trick customers into visiting a malicious URL and hand over their credentials, that are subsequently relayed to the risk actors in real-time by way of a Telegram channel, granting them unauthorized entry to their accounts. The social engineering efforts are properly deliberate, with the attackers conducting reconnaissance on the targets and crafting custom-made phishing pages.
The kits, bought on an as-a-service foundation, come fitted with client-side scripts that make it potential for risk actors to manage the authentication circulation within the browser of a focused person in real-time, as they supply verbal directions and persuade them to take actions (e.g., approve push notifications or enter one-time passwords) that will result in an MFA bypass.
“Utilizing these kits, an attacker on the telephone to a focused person can management the authentication circulation as that person interacts with credential phishing pages,” mentioned Moussa Diallo, risk researcher at Okta Menace Intelligence. “They will management what pages the goal sees of their browser in good synchronization with the directions they’re offering on the decision. The risk actor can use this synchronization to defeat any type of MFA that isn’t phishing-resistant.”
In current weeks, phishing campaigns have exploited Fundamental Authentication URLs (i.e., “username:password@area[.]com”) by putting a trusted area within the username area, adopted by an @ image and the precise malicious area to visually mislead the sufferer.
“When a person sees a URL that begins with a well-recognized and trusted area, they might assume the hyperlink is respectable and secure to click on,” Netcraft mentioned. “Nevertheless, the browser interprets all the pieces earlier than the @ image as authentication credentials, not as a part of the vacation spot. The actual area, or the one which the browser connects to, is included after the @ image.”
Different campaigns have resorted to easy visible deception tips like utilizing “rn” rather than “m” to hide malicious domains and deceive victims into pondering they’re visiting a respectable area related to firms like Microsoft (“rnicrosoft[.]com”), Mastercard (“rnastercard[.]de”), Marriott (“rnarriotthotels[.]com”), and Mitsubishi (“rnitsubishielectric[.]com”). That is referred to as a homoglyph assault.
“Whereas attackers usually goal at manufacturers that begin with the letter M for this system, among the most convincing domains come from swapping an inner ‘m’ with ‘rn’ inside phrases,” Netcraft’s Ivan Khamenka mentioned. “This system turns into much more harmful when it seems in phrases that organizations generally use as a part of their model, subdomains, or service identifiers. Phrases like electronic mail, message, member, affirmation, and communication all include mid-word m’s that customers barely course of.”