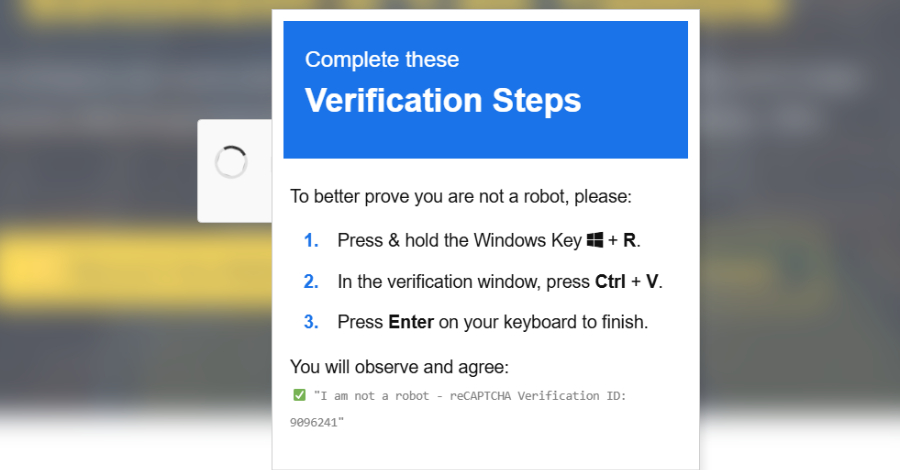
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed particulars of a brand new marketing campaign that mixes ClickFix-style pretend CAPTCHAs with a signed Microsoft Utility Virtualization (App-V) script to distribute an data stealer referred to as Amatera.
“As an alternative of launching PowerShell instantly, the attacker makes use of this script to regulate how execution begins and to keep away from extra frequent, simply acknowledged execution paths,” Blackpoint researchers Jack Patrick and Sam Decker stated in a report revealed final week.
In doing so, the thought is to rework the App-V script right into a living-off-the-land (LotL) binary that proxies the execution of PowerShell by means of a trusted Microsoft element to hide the malicious exercise.
The start line of the assault is a pretend CAPTCHA verification immediate that seeks to trick customers into pasting and executing a malicious command on the Home windows Run dialog. However right here is the place the assault diverges from conventional ClickFix assaults.
The provided command, quite than invoking PowerShell instantly, abuses “SyncAppvPublishingServer.vbs,” a signed Visible Primary Script related to App-V to retrieve and execute an in-memory loader from an exterior server utilizing “wscript.exe.”
It is value noting that the misuse of “SyncAppvPublishingServer.vbs” isn’t new. In 2022, two totally different menace actors from China and North Korea, tracked as DarkHotel and BlueNoroff, have been noticed leveraging the LOLBin exploit to stealthily execute a PowerShell script. However that is the primary time it has been noticed in ClickFix assaults.
“Adversaries could abuse SyncAppvPublishingServer.vbs to bypass PowerShell execution restrictions and evade defensive counter measures by ‘residing off the land,'” MITRE notes in its ATT&CK framework. “Proxying execution could perform as a trusted/signed different to instantly invoking ‘powershell.exe.'”
The usage of an App-V script can be important because the virtualization resolution is constructed solely into Enterprise and Schooling editions of Home windows 10 and Home windows 11, together with trendy Home windows Server variations. It is not out there for Home windows Residence or Professional installations.
In Home windows working programs the place App-V is both absent or not enabled, the execution of the command fails outright. This additionally signifies that enterprise managed programs are possible the first targets of the marketing campaign.
The obfuscated loader runs checks to make sure that it is not run inside sandboxed environments, after which proceeds to fetch configuration information from a public Google Calendar (ICS) file, primarily turning a trusted third-party service right into a useless drop resolver.
“By externalizing configuration on this manner, the actor can quickly rotate infrastructure or modify supply parameters with out redeploying earlier levels of the chain, decreasing operational friction and increasing the lifespan of the preliminary an infection vector,” the researchers identified.
Parsing the calendar occasion file results in the retrieval of extra loader levels, together with a PowerShell script that capabilities as an intermediate loader to execute the following stage, one other PowerShell script, instantly in reminiscence. This step, in flip, ends in the retrieval of a PNG picture from domains like “gcdnb.pbrd[.]co” and “iili[.]io” by way of WinINet APIs that conceals an encrypted and compressed PowerShell payload.
The ensuing script is decrypted, GZip decompressed in reminiscence, and run utilizing Invoke-Expression, finally culminating within the execution of a shellcode loader that is designed to launch Amatera Stealer.
“What makes this marketing campaign fascinating is not any single trick, however how rigorously thought-out every little thing is when chained collectively,” Blackpoint concluded. “Every stage reinforces the final, from requiring guide consumer interplay, to validating clipboard state, to pulling dwell configuration from a trusted third-party service.”
“The result’s an execution circulation that solely progresses when it unfolds (virtually) precisely because the attacker expects, which makes each automated detonation and informal evaluation considerably more durable.”
The Evolution of ClickFix: JackFix, CrashFix, and GlitchFix
The disclosure comes as ClickFix has turn out to be probably the most broadly used preliminary entry strategies within the final 12 months, accounting for 47% of the assaults noticed by Microsoft.
Current ClickFix campaigns have focused social media content material creators by claiming they’re eligible free of charge verified badges, instructing them by way of movies to repeat authentication tokens from their browser cookies right into a pretend type to finish the supposed verification course of. The embedded video additionally informs the consumer to “not log off for a minimum of 24 hours” to maintain the authentication tokens legitimate.
The marketing campaign, energetic since a minimum of September 2025, is estimated to have used 115 internet pages throughout the assault chain and eight exfiltration endpoints, per Hunt.io. The primary targets of the exercise embody creators, monetized pages, and companies in search of verification, with the top aim being to facilitate account takeover following token theft.
“Defending in opposition to the ClickFix method is uniquely difficult as a result of the assault chain is constructed virtually fully on professional consumer actions and the abuse of trusted system instruments,” Martin Zugec, technical options director at Bitdefender, stated in a report final month. “Not like conventional malware, ClickFix turns the consumer into the preliminary entry vector, making the assault look benign from an endpoint protection perspective.”
ClickFix can be consistently evolving, using variants like JackFix and CrashFix to deceive the sufferer into infecting their very own machines. Whereas operators use a number of strategies to try to persuade a goal to carry out command execution, the rising reputation of the social engineering method has paved the way in which for ClickFix builders which might be marketed on hacker boards for anyplace between $200 to $1,500 per 30 days.
The most recent entrant to this menace panorama is ErrTraffic, a site visitors distribution system (TDS) that is particularly designed for ClickFix-like campaigns by inflicting compromised web sites injected with malicious JavaScript to glitch after which suggesting a repair to deal with the non-existent downside. This system has been codenamed GlitchFix.
The malware-as-a-service (MaaS) helps three totally different file distribution modes that contain utilizing pretend browser replace alerts, pretend “system font required” dialogs, and bogus lacking system font errors to set off the execution of malicious instructions. ErrTraffic is explicitly blocked from working on machines situated within the Commonwealth of Impartial States (CIS) nations.
“ErrTraffic does not simply present a pretend replace immediate, it actively corrupts the underlying web page to make victims consider one thing is genuinely mistaken,” Censys stated. “It additionally applies CSS transformations that make every little thing look damaged.”
ClickFix has additionally been adopted by menace actors behind the ClearFake marketing campaign, which is thought to contaminate websites with pretend internet browser replace decoys on compromised WordPress to distribute malware. ClearFake’s use of ClickFix was first recorded in Might 2024, leveraging CAPTCHA challenges for delivering Emmenhtal Loader (aka PEAKLIGHT), which then drops Lumma Stealer.
The assault chain additionally makes use of one other recognized method known as EtherHiding to retrieve the next-stage JavaScript code utilizing sensible contracts on Binance’s BNB Sensible Chain (BSC) and ultimately inject the ClickFix pretend CAPTCHA obtained from a unique sensible contract into the online web page. On the identical time, the ultimate stage avoids re-infecting already contaminated victims.
Like within the case of the Amatera Stealer assault, the ClickFix command copied to the clipboard abuses “SyncAppvPublishingServer.vbs” to acquire the ultimate payload hosted on the jsDelivr content material supply community (CDN). Expel’s evaluation of the ClearFake marketing campaign reveals that as many as 147,521 programs have possible been contaminated since late August 2025.
“One in every of many components safety merchandise use to resolve if habits is malicious or not is whether or not stated habits is being carried out by a trusted software,” safety researcher Marcus Hutchins stated. “On this case, ‘SyncAppvPublishingServer.vbs’ is a default Home windows element, and the file can solely be modified by TrustedInstaller (a extremely privileged system account used internally by the working system). Due to this fact, the file and its habits alone wouldn’t usually be suspect.”
“Organizations and EDR are unlikely to outright block SyncAppvPublishingServer.vbs from launching PowerShell in hidden mode, as it will forestall the element from getting used for its supposed function. Consequently, by abusing the command line injection bug in SyncAppvPublishingServer.vbs, attackers can execute arbitrary code by way of a trusted system element.”
Expel additionally characterised the marketing campaign as extremely refined and really evasive, owing to the usage of in-memory PowerShell code execution, coupled with its reliance on blockchain and common CDNs, thus guaranteeing that it doesn’t talk with any infrastructure that is not a professional service.
Censys has described the broader pretend CAPTCHA ecosystem as a “fragmented, fast-changing abuse sample that makes use of trusted internet infrastructure because the supply floor,” whereby Cloudflare-style challenges act as a conduit for clipboard-driven execution of PowerShell instructions, VB Scripts, MSI installers, and even hand-offs to browser-native frameworks like Matrix Push C2.
“This aligns with a broader shift towards Dwelling Off the Net: systematic reuse of security-themed interfaces, platform-sanctioned workflows, and conditioned consumer habits to ship malware,” the assault floor administration agency stated. “Attackers don’t must compromise trusted providers; they inherit belief by working inside acquainted verification and browser workflows that customers and tooling are educated to just accept.”