In the early days of January 2026, a sophisticated cyberattack targeting the financial sector emerged, notable for its ability to penetrate corporate environments without triggering conventional security alerts. The campaign executed by APT-Q-27 was marked by its subtlety, allowing attackers to evade detection by both end-users and standard endpoint security systems.
Stealthy Infiltration and Social Engineering
The attack’s success hinged on its stealthy approach, which bypassed traditional defenses critical to maintaining data integrity and operational trust within organizations. The breach was traced to a corporate customer support department where an employee interacted with a malicious link disguised within a Zendesk ticket. This link masqueraded as a harmless image file but instead initiated the download of an executable posing as a “.pif” file. The use of social engineering was pivotal, as Windows systems often conceal known file extensions, making the file appear as a legitimate image or document.
Technical Analysis of the Attack
CyStack analysts uncovered the malware through an extensive forensic examination of an affected workstation. They identified similarities between this campaign and previous operations linked to the APT-Q-27 group, also known as GoldenEyeDog. The malware showcased a revoked digital signature from “Portier Global Pty Ltd,” but the presence of a valid timestamp allowed the file to bypass Windows SmartScreen filters.
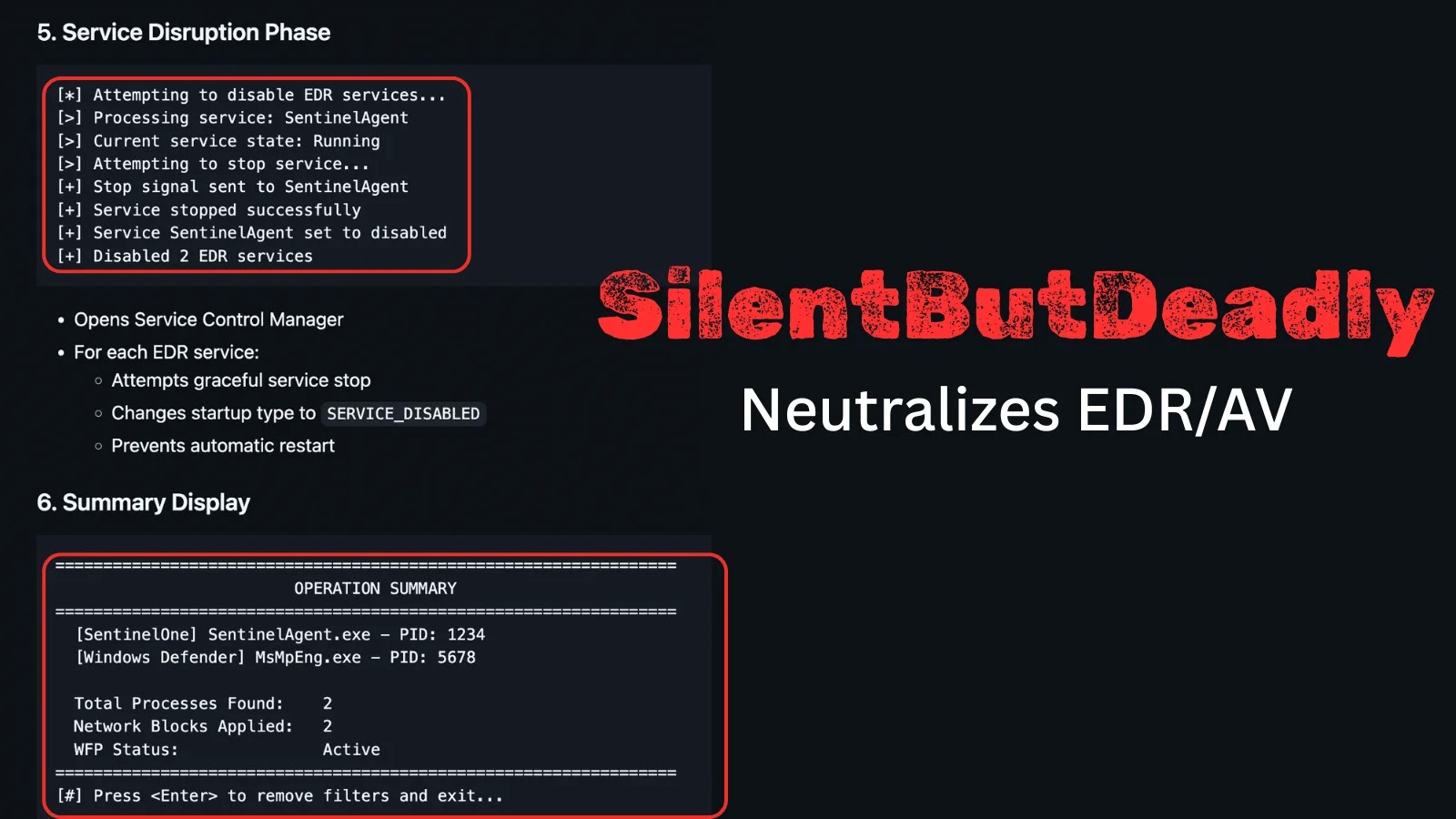
Advanced Evasion Techniques
A notable aspect of this attack was its advanced evasion methods, including DLL sideloading and in-memory execution. The malware’s dropper established a staging directory mimicking a Windows Update cache to blend with legitimate system files. Within this directory, a signed, benign executable loaded a malicious DLL named crashreport.dll, enabling the execution of the final payload entirely in memory, thus avoiding detectable file creation.
This technique allowed the attackers to operate within trusted processes, enabling command receipt and additional module downloads while remaining undetected by many file-based scanning tools.
Defensive Measures and Recommendations
To counter such stealthy intrusions, CyStack advises enterprises to implement proactive threat hunting focused on detecting abnormal process behaviors, such as unexpected DLL loads. Maintaining incident response readiness to swiftly isolate affected systems is crucial before threats can spread. Organizations are encouraged to adopt behavior-based endpoint protections over simple signature reliance and to use contextual threat intelligence to pinpoint campaign-specific indicators. Additionally, reviewing unconventional attack surfaces like customer support systems is essential to close potential security gaps.
For ongoing updates on cybersecurity news, follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X, and consider setting CSN as your preferred source on Google.