Aug 20, 2025Ravie LakshmananVulnerability / Browser Safety
Widespread password supervisor plugins for net browsers have been discovered prone to clickjacking safety vulnerabilities that could possibly be exploited to steal account credentials, two-factor authentication (2FA) codes, and bank card particulars below sure situations.
The approach has been dubbed Doc Object Mannequin (DOM)-based extension clickjacking by unbiased safety researcher Marek Tóth, who offered the findings on the DEF CON 33 safety convention earlier this month.
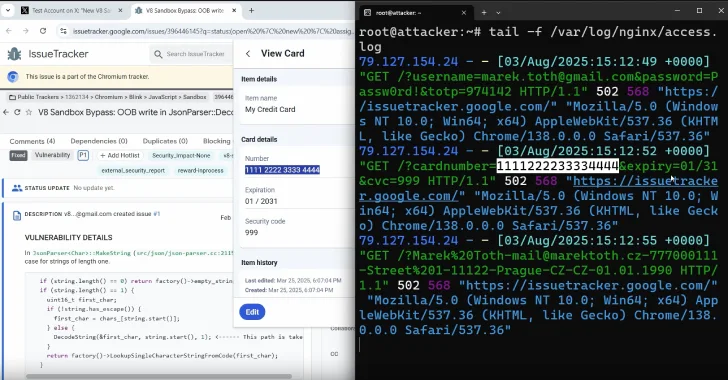
“A single click on wherever on an attacker-controlled web site may permit attackers to steal customers’ knowledge (bank card particulars, private knowledge, login credentials, together with TOTP),” Tóth stated. “The brand new approach is common and could be utilized to different sorts of extensions.”
Clickjacking, additionally referred to as UI redressing, refers to a kind of assault through which customers are tricked into performing a collection of actions on an internet site that seem ostensibly innocent, similar to clicking on buttons, when, in actuality, they’re inadvertently finishing up the attacker’s bidding.
The brand new approach detailed by Tóth primarily includes utilizing a malicious script to control UI components in an internet web page that browser extensions inject into the DOM — for instance, auto-fill prompts, by making them invisible by setting their opacity to zero.
The analysis particularly targeted on 11 standard password supervisor browser add-ons, starting from 1Password to iCloud Passwords, all of which have been discovered to be prone to DOM-based extension clickjacking. Collectively, these extensions have hundreds of thousands of customers.
To tug off the assault, all a nasty actor has to do is create a faux website with an intrusive pop-up, similar to a login display or a cookie consent banner, whereas embedding an invisible login kind such that clicking on the positioning to shut the pop-up causes the credential info to be auto-filled by the password supervisor and exfiltrated to a distant server.
“All password managers crammed credentials not solely to the ‘principal’ area, but in addition to all subdomains,” Tóth defined. “An attacker may simply discover XSS or different vulnerabilities and steal the consumer’s saved credentials with a single click on (10 out of 11), together with TOTP (9 out of 11). In some situations, passkey authentication is also exploited (8 out of 11).”
Following accountable disclosure, six of the distributors have but to launch fixes for the defect –
1Password Password Supervisor 8.11.4.27
Apple iCloud Passwords 3.1.25
Bitwarden Password Supervisor 2025.7.0
Enpass 6.11.6
LastPass 4.146.3
LogMeOnce 7.12.4
Software program provide chain safety agency Socket, which independently reviewed the analysis, stated Bitwarden, Enpass, and iCloud Passwords are actively engaged on fixes, whereas 1Password and LastPass marked them as informative. It has additionally reached out to US-CERT to assign CVE identifiers for the recognized points.
Till fixes can be found, it is suggested that customers disable the auto-fill perform of their password managers and solely use copy/paste.
“For Chromium-based browser customers, it’s endorsed to configure website entry to ‘on click on’ in extension settings,” Tóth stated. “This configuration permits customers to manually management auto-fill performance.”