Aug 26, 2025Ravie Lakshmanan
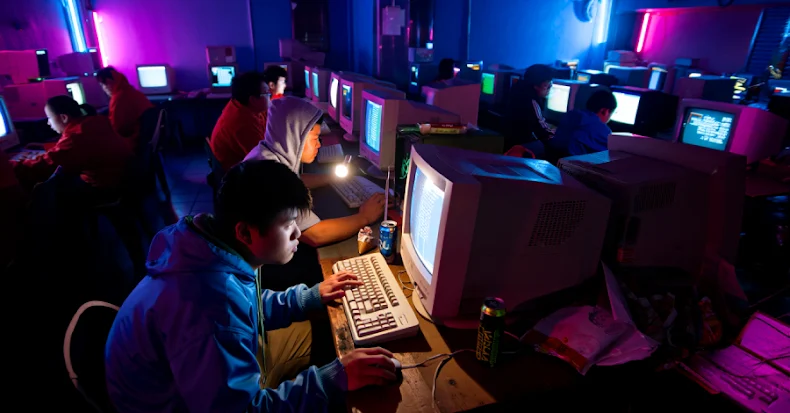
Cybersecurity researchers have found a brand new variant of an Android banking trojan known as HOOK that options ransomware-style overlay screens to show extortion messages.
“A outstanding attribute of the newest variant is its capability to deploy a full-screen ransomware overlay, which goals to coerce the sufferer into remitting a ransom cost,” Zimperium zLabs researcher Vishnu Pratapagiri stated. “This overlay presents an alarming ‘*WARNING*’ message, alongside a pockets tackle and quantity, each of that are dynamically retrieved from the command-and-control server.”
The cellular safety firm stated the overlay is remotely initiated when the command “ransome” is issued by the C2 server. The overlay could be dismissed by the attacker by sending the “delete_ransome” command.
HOOK is assessed to be an offshoot of the ERMAC banking trojan, which, coincidentally, had its supply code leaked on a publicly accessible listing over the web.
Like different banking malware focusing on Android, it is able to displaying a faux overlay display on high of monetary apps to steal customers’ credentials and abuse Android accessibility companies to automate fraud and commandeer gadgets remotely.
Different notable options embody the power to ship SMS messages to specified telephone numbers, stream the sufferer’s display, seize photographs utilizing the front-facing digicam, and steal cookies and restoration phrases related to cryptocurrency wallets.
The newest model, per Zimperium, indicators a significant step ahead, supporting 107 distant instructions, with 38 newly added ones. This consists of serving clear overlays to seize consumer gestures, faux NFC overlays to trick victims into sharing delicate information, and misleading prompts to assemble lockscreen PIN or sample.
The checklist of newly added instructions is as follows –
takenfc, to show a faux NFC scanning display utilizing a fullscreen WebView overlay and browse card information
unlock_pin, to show a faux machine unlock display to gather unlock sample or PIN code and acquire unauthorized entry to the machine
takencard, to show a faux overlay to gather bank card data by mimicking a Google Pay interface
start_record_gesture, to file consumer gestures by displaying a clear full display overlay
HOOK is believed to be distributed on a big scale, utilizing phishing web sites and bogus GitHub repositories to host and disseminate malicious APK information. Among the different Android malware households distributed through GitHub embody ERMAC and Brokewell, indicating a broader adoption amongst risk actors.
“The evolution of HOOK illustrates how banking trojans are quickly converging with adware and ransomware ways, blurring risk classes,” Zimperium famous. “With steady function growth and broad distribution, these households pose a rising danger to monetary establishments, enterprises, and finish customers alike.”
Anatsa Continues to Evolve
The disclosure comes as Zscaler’s ThreatLabs detailed an up to date model of the Anatsa banking trojan that has now expanded its focus to focus on over 831 banking and cryptocurrency companies worldwide, together with these in Germany and South Korea, up from 650 reported beforehand.
One of many apps in query has been discovered to imitate a file supervisor app (package deal title: “com.synexa.fileops.fileedge_organizerviewer”), which acts as a dropper to ship Anatsa. In addition to changing dynamic code loading of distant Dalvik Executable (DEX) payloads with direct set up of the trojan, the malware makes use of corrupted archives to cover the DEX payload that is deployed throughout runtime.
Anatsa additionally requests permissions for Android’s accessibility companies, which it subsequently abuses to grant itself further permissions that enable it to ship and obtain SMS messages, in addition to draw content material on high of different purposes to show overlay home windows.
In all, the corporate stated it recognized 77 malicious apps from varied adware, maskware, and malware households, similar to Anatsa, Joker, and Harly, within the Google Play Retailer, accounting for over 19 million installations. Maskware refers to a class of apps that current themselves as respectable purposes or video games to app shops however incorporate obfuscation, dynamic code loading, or cloaking strategies to hide malicious content material.
Harly is a variant of Joker that was first flagged by Kaspersky in 2022. Earlier this March, Human Safety stated it uncovered 95 malicious purposes containing Harly that had been hosted within the Google Play Retailer.
“Anatsa continues to evolve and enhance with anti-analysis strategies to higher evade detection,” safety researcher Himanshu Sharma stated. “The malware has additionally added help for greater than 150 new monetary purposes to focus on.”