Sep 16, 2025Ravie LakshmananHardware Safety / Vulnerability
A staff of lecturers from ETH Zürich and Google has found a brand new variant of a RowHammer assault concentrating on Double Information Fee 5 (DDR5) reminiscence chips from South Korean semiconductor vendor SK Hynix.
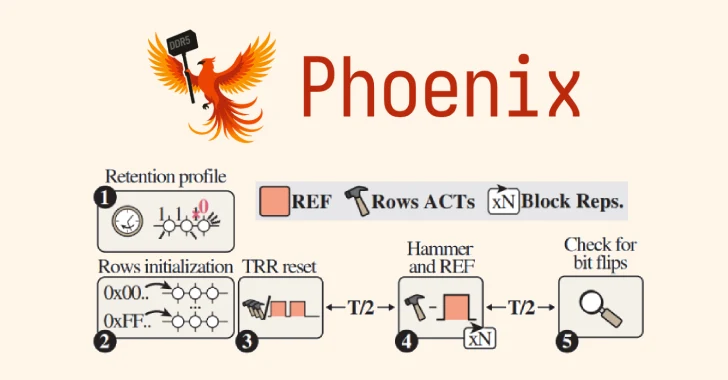
The RowHammer assault variant, codenamed Phoenix (CVE-2025-6202, CVSS rating: 7.1), is able to bypassing refined safety mechanisms put in place to withstand the assault.
“We now have confirmed that reliably triggering RowHammer bit flips on DDR5 units from SK Hynix is feasible on a bigger scale,” ETH Zürich mentioned. “We additionally proved that on-die ECC doesn’t cease RowHammer, and RowHammer end-to-end assaults are nonetheless potential with DDR5.”
RowHammer refers to a {hardware} vulnerability the place repeated entry of a row of reminiscence in a DRAM chip can set off bit flips in adjoining rows, leading to information corruption. This may be subsequently weaponized by dangerous actors to achieve unauthorized entry to information, escalate privileges, and even trigger a denial-of-service.
Though first demonstrated in 2014, future DRAM chips usually tend to be vulnerable to RowHammer assaults as DRAM producers rely on density scaling to extend DRAM capability.
In a research revealed by ETH Zürich researchers in 2020, it was discovered that “newer DRAM chips are extra susceptible to RowHammer: as gadget characteristic dimension reduces, the variety of activations wanted to induce a RowHammer bit flip additionally reduces.”
Additional analysis into the topic has demonstrated that the vulnerability has a number of dimensions to it and that it is delicate to a number of variables, together with environmental situations (temperature and voltage), course of variation, saved information patterns, reminiscence entry patterns, and reminiscence management insurance policies.
Among the main mitigations for RowHammer assaults embrace Error Correction Code (ECC) and Goal Row Refresh (TRR). Nevertheless, these countermeasures have been confirmed to be ineffective towards extra refined assaults like TRRespass, SMASH, Half-Double, and Blacksmith.
The newest findings from ETH Zürich and Google present that it is potential to bypass superior TRR defenses on DDR5 reminiscence, opening the door for what the researchers name the “first-ever RowHammer privilege escalation exploit on a regular, production-grade desktop system geared up with DDR5 reminiscence.”
In different phrases, the tip result’s a privilege escalation exploit that obtains root on a DDR5 system with default settings in as little as 109 seconds. Particularly, the assault takes benefit of the truth that mitigation doesn’t pattern sure refresh intervals to flip bits on all 15 DDR5 reminiscence chips within the take a look at pool that have been produced between 2021 and 2024.
Potential exploitation eventualities involving these bit flips permit for concentrating on RSA-2048 keys of a co-located digital machine to interrupt SSH authentication, in addition to utilizing the sudo binary to escalate native privileges to the foundation consumer.
“As DRAM units within the wild can’t be up to date, they are going to stay susceptible for a few years,” the researchers mentioned. “We advocate rising the refresh charge to 3x, which stopped Phoenix from triggering bit flips on our take a look at programs.”
The disclosure comes weeks after analysis groups from George Mason College and Georgia Institute of Expertise detailed two completely different RowHammer assaults referred to as OneFlip and ECC.fail, respectively.
Whereas OneFlip revolves round triggering a single bit flip to change Deep Neural Community (DNN) mannequin weights and activate unintended habits, ECC.fail is described as the primary end-to-end RowHammer assault that is efficient towards DDR4 server machines with ECC reminiscence.
“Not like their PC counterparts, servers have further protections towards reminiscence information corruptions (e.g., RowHammer or cosmic ray bit flips), within the type of error correcting codes,” the researchers mentioned. “These can detect bit flips in reminiscence, and even probably right them. ECC.fail bypasses these protections by rigorously inducing RowHammer bit flips at sure reminiscence places.”