Menace actors are leveraging the legacy Home windows error‐reporting utility WerFaultSecure.exe to extract the reminiscence area of the Native Safety Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS.EXE) and harvest cached credentials from totally patched Home windows 11 24H2 methods.
After gaining preliminary entry to a number, adversaries steadily search to dump LSASS reminiscence to escalate privileges and transfer laterally throughout the community.
Trendy Home windows severely restricts direct reminiscence entry to LSASS by implementing Protected Course of Mild (PPL), requiring kernel privilege or a peer PPL course of for interplay.
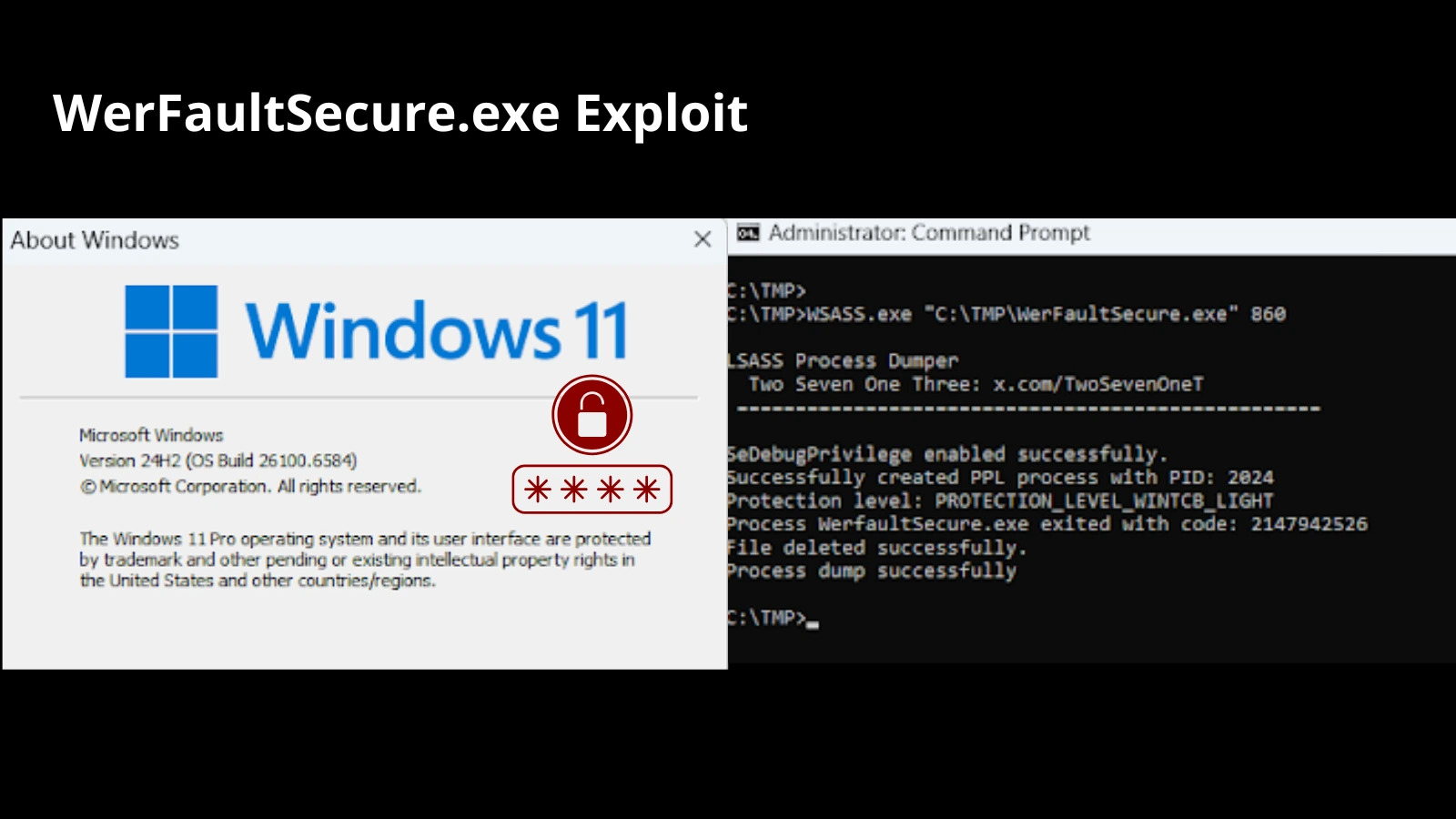
Zero Salarium researchers have now demonstrated easy methods to bypass these defenses by operating a weak WerFaultSecure.exe binary compiled for Home windows 8.1 beneath Home windows 11, thereby acquiring an unencrypted reminiscence dump of LSASS.
Leveraging WerFaultSecure.exe’s PPL Privilege
WerFaultSecure.exe is a part of the Home windows Error Reporting (WER) framework and usually executes with the very best PPL label, WinTCB, to gather crash dumps from protected processes.
Its protected standing permits it to entry LSASS reminiscence beneath the guise of a crash handler.
In Home windows 8.1, a flaw existed whereby WerFaultSecure.exe might be imposed into writing crash dumps with out making use of its constructed‐in encryption routines, leading to unencrypted dump recordsdata on disk.
Exploiting WerFaultSecure.exe
By copying the weak WerFaultSecure.exe from Home windows 8.1 onto a Home windows 11 24H2 machine and launching it with PPL elevation, attackers can trick the instrument into capturing LSASS reminiscence and writing a uncooked dump.
Zero Salarium studies that the exploit sequence entails operating WerFaultSecure.exe with undocumented switches found via reverse engineering: /h to invoke safe hidden crash mode, /pid [pid] to focus on the LSASS course of, /tid [tid] to specify its major thread, and /file [handle] to designate an unencrypted output deal with.
The attacker makes use of a customized loader named WSASS to spawn WerFaultSecure.exe through the CreateProcessAsPPL API, inheriting handles for the crash dump and occasion objects.
WSASS waits for dump completion, then replaces the primary 4 bytes of the generated file (from the PNG magic header) with the MDMP signature (0x4D,0x44,0x4D,0x50) so it masquerades as a benign picture system and evades antivirus checks.
MDMP changed
Lastly, the loader resumes any suspended threads in LSASS by issuing minimal PROCESS_SUSPEND_RESUME rights to revive system stability.
As soon as the attacker restores the MDMP header, the ensuing minidump may be loaded into commonplace instruments, reminiscent of pypykatz or Mimikatz, to extract NTLM hashes and plaintext credentials, facilitating additional lateral motion.
This system underscores the significance of monitoring WerFaultSecure.exe binaries outdoors the System32 listing and validating PPL‐protected course of invocations to detect anomalous conduct early.
This exploit demonstrates how backward compatibility in Home windows may be leveraged towards trendy defenses, highlighting the necessity for defenders to observe each file places and invocation contexts of error-reporting instruments.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X for each day cybersecurity updates. Contact us to function your tales.