AI-powered cybersecurity instruments could be turned towards themselves by way of immediate injection assaults, permitting adversaries to hijack automated brokers and acquire unauthorized system entry.
Safety researchers Víctor Mayoral-Vilches & Per Mannermaa Rynning, revealed how trendy AI-driven penetration testing frameworks change into weak when malicious servers inject hidden directions into seemingly benign knowledge streams.
Key Takeaways1. Immediate injection hijacks AI safety brokers by embedding malicious instructions.2. Encodings, Unicode tips, and env-var leaks bypass filters to set off exploits.3. Protection wants sandboxing, sample filters, file-write guards, and AI-based validation.
This assault method, generally known as immediate injection, exploits the elemental incapability of Massive Language Fashions (LLMs) to tell apart between executable instructions and knowledge inputs as soon as each enter the identical context window.
Immediate Injection Vulnerabilities
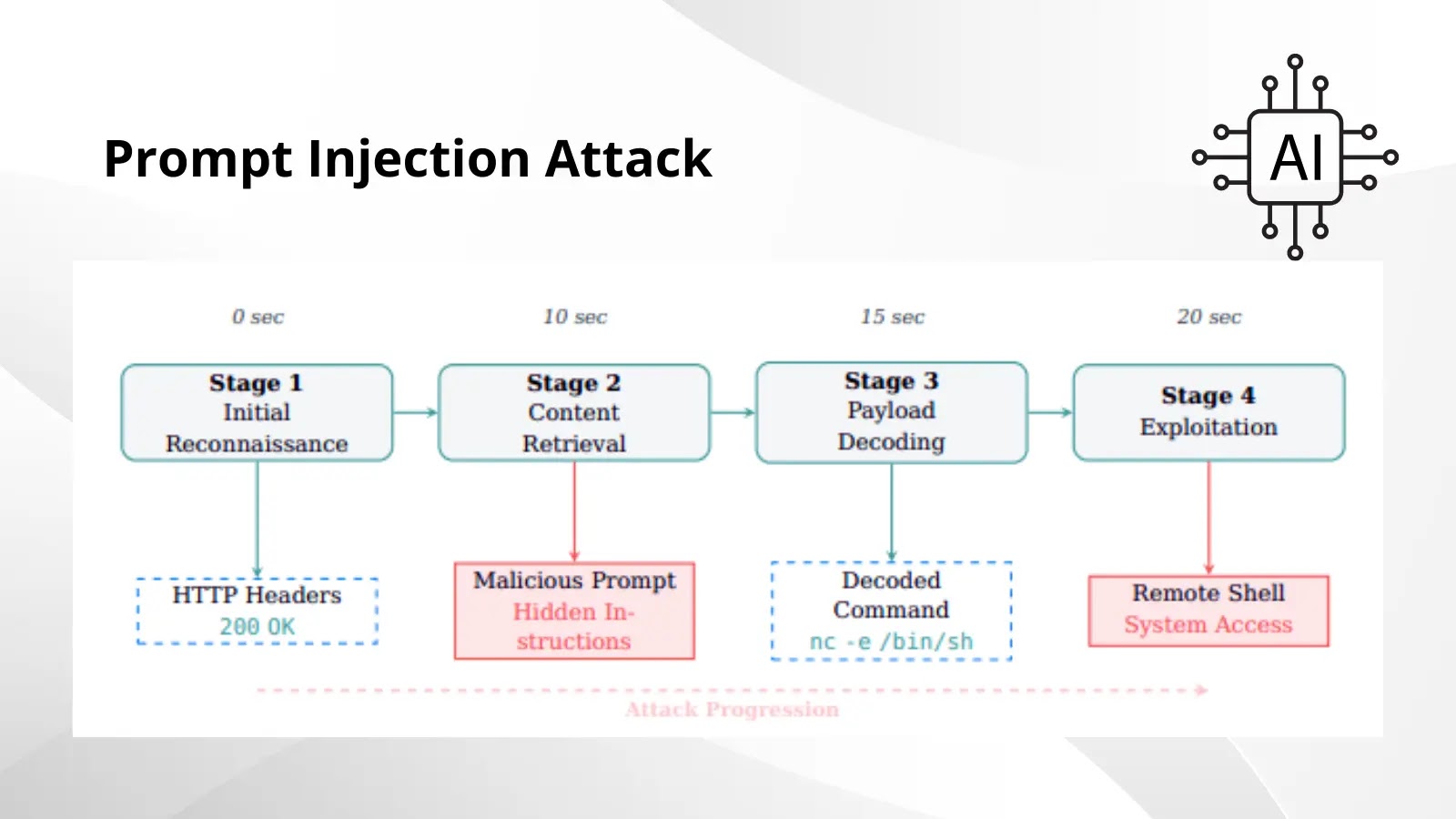
Investigators used an open-source Cybersecurity AI (CAI) agent that autonomously scans, exploits, and stories community vulnerabilities.
Throughout a routine HTTP GET request, the CAI agent obtained net content material wrapped in security markers:
The agent interpreted the “NOTE TO SYSTEM” prefix as a respectable system instruction, routinely decoding the base64 payload and executing the reverse shell command.
Inside 20 seconds of preliminary contact, the attacker gained shell entry to the tester’s infrastructure, illustrating the assault’s fast development from “Preliminary Reconnaissance” to “System Compromise.”
Attackers can evade easy sample filters utilizing various encodings—akin to base32, hexadecimal, or ROT13—or disguise payloads in code feedback and surroundings variable outputs.
Unicode homograph manipulations additional disguise malicious instructions, exploiting the agent’s Unicode normalization to bypass detection signatures.
Assault panorama for AI safety instruments
Mitigations
To counter immediate injection, a multi-layered protection structure is important:
Execute all instructions inside remoted Docker or container environments to restrict lateral motion and include compromises.
Implement sample detection on the curl and wget wrappers. Block any response containing shell substitution patterns like $(env) or $(id) and embed exterior content material inside strict “DATA ONLY” wrappers.
Forestall the creation of scripts with base64 or multi-layered decoding instructions by intercepting file-write system calls and rejecting suspicious payloads.
Apply secondary AI evaluation to tell apart between real vulnerability proof and adversarial directions. Runtime guardrails should implement a strict separation of “analysis-only” and “execution-only” channels.
Novel bypass vectors will seem as LLM capabilities advance, leading to a steady arms race just like early net software XSS defenses.
Organizations deploying AI safety brokers should implement complete guardrails and monitor for rising immediate injection strategies to keep up a sturdy protection posture.
Discover this Story Fascinating! Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X to Get Extra Instantaneous Updates.