Essential vulnerabilities in Apache Tomcat and Apache Camel are being actively exploited by cybercriminals worldwide, with safety researchers documenting over 125,000 assault makes an attempt throughout greater than 70 nations since their disclosure in March 2025.
The three vulnerabilities—CVE-2025-24813 affecting Apache Tomcat and CVE-2025-27636 and CVE-2025-29891 impacting Apache Camel—allow distant code execution and pose vital dangers to organizations operating these widely-deployed Java-based platforms.
Apache Tomcat, the favored net server platform that permits Java-based net purposes, is susceptible by way of CVE-2025-24813, which impacts variations 9.0.0.M1 to 9.0.98, 10.1.0-M1 to 10.1.34, and 11.0.0-M1 to 11.0.2.
The flaw exploits Tomcat’s partial PUT performance mixed with session persistence options, permitting attackers to govern serialized session information and obtain arbitrary code execution.
Apache Camel, an integration framework for connecting various techniques, suffers from two associated vulnerabilities that allow attackers to bypass header filtering mechanisms by way of case-sensitive manipulation strategies.
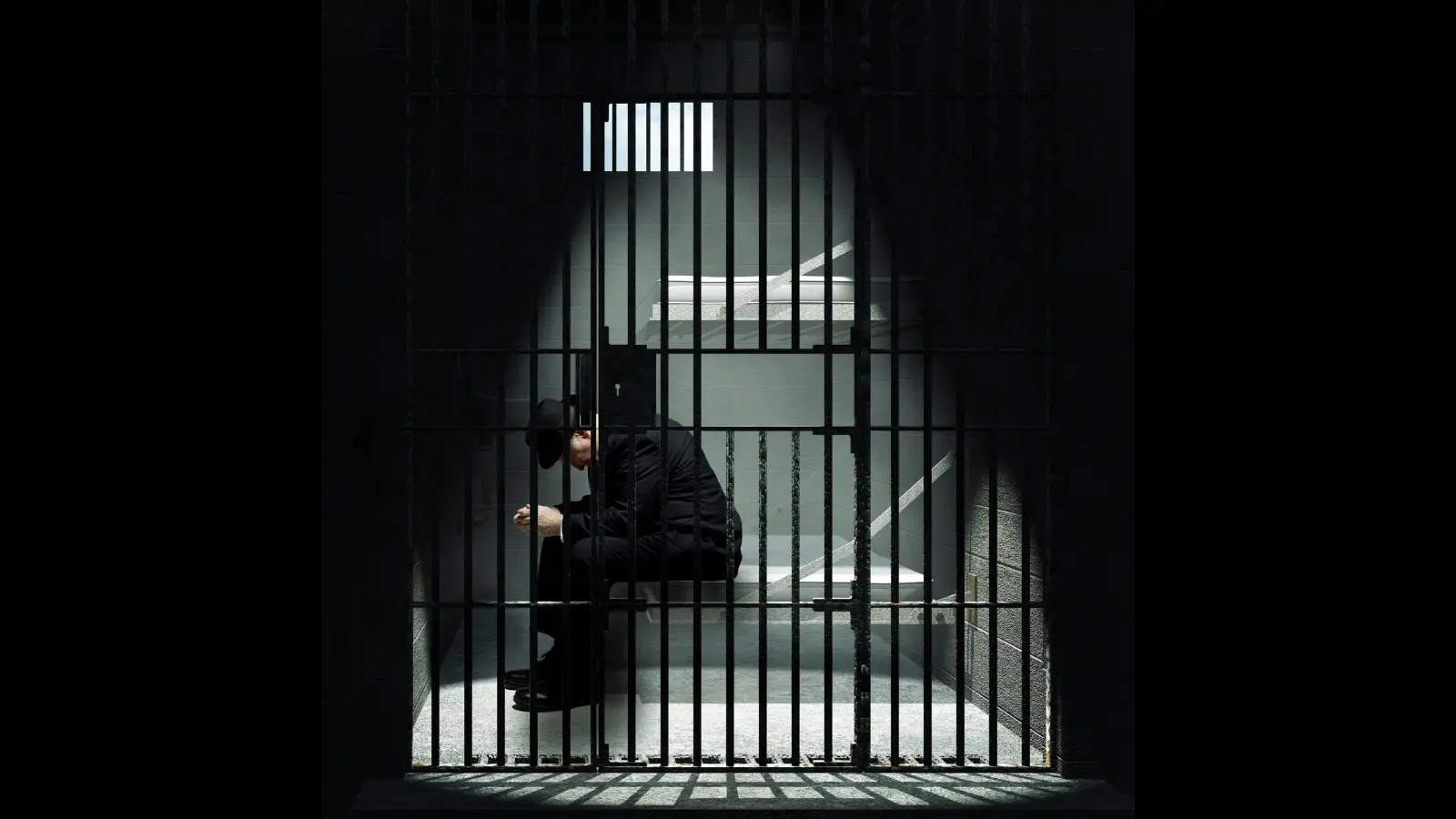
Two steps of the exploit (Supply – Palo Alto Networks)
Palo Alto Networks researchers recognized a dramatic surge in exploitation makes an attempt instantly following the vulnerabilities’ public disclosure, with assault frequency peaking inside the first week of March 2025.
The safety agency’s telemetry techniques blocked 125,856 probes, scans, and exploit makes an attempt, together with 7,859 particularly concentrating on the Tomcat vulnerability.
Evaluation of the assault patterns reveals each automated scanning instruments and lively exploitation makes an attempt, with many assaults using the freely out there Nuclei Scanner framework.
The risk panorama has developed quickly because the preliminary disclosures, with proof-of-concept exploits changing into publicly out there shortly after Apache launched safety patches.
Cached session file (Supply – Palo Alto Networks)
The benefit of exploitation has lowered the barrier for much less subtle risk actors, making these vulnerabilities significantly harmful for organizations that haven’t utilized vital updates.
Tomcat’s Partial PUT Exploitation Mechanism
The CVE-2025-24813 vulnerability leverages a classy two-step assault course of that exploits Tomcat’s dealing with of partial PUT requests with Content material-Vary headers.
Attackers first stage their malicious payload by sending an HTTP PUT request containing serialized malicious code, with the filename ending in “.session” to make sure correct caching by Tomcat’s session persistence mechanism.
The preliminary payload deployment requires particular server configurations, together with a disabled readonly parameter and enabled session persistence.
When these situations are met, Tomcat saves the attacker’s serialized code to 2 places: a traditional cache file beneath the webapps listing and a brief file with a number one interval within the work listing.
The exploitation course of concludes when the attacker sends a follow-up HTTP GET request containing a rigorously crafted JSESSIONID cookie worth that triggers deserialization of the cached malicious code.
Examine stay malware conduct, hint each step of an assault, and make sooner, smarter safety choices -> Attempt ANY.RUN now