A brand new and complicated phishing marketing campaign is focusing on distant staff and IT directors by impersonating the official Fortinet VPN obtain portal.
This assault is especially harmful as a result of it leverages SEO (web optimization) and, alarmingly, AI-generated search summaries to lure victims right into a entice.
The marketing campaign makes use of a multi-stage redirect mechanism beginning with trusted domains to bypass preliminary safety filters, in the end stealing VPN credentials and distributing malware.
Safety researcher with Alias G0njxa has noticed that fashionable search engines like google, which now function AI-generated “fast solutions” or summaries, are inadvertently boosting this marketing campaign.
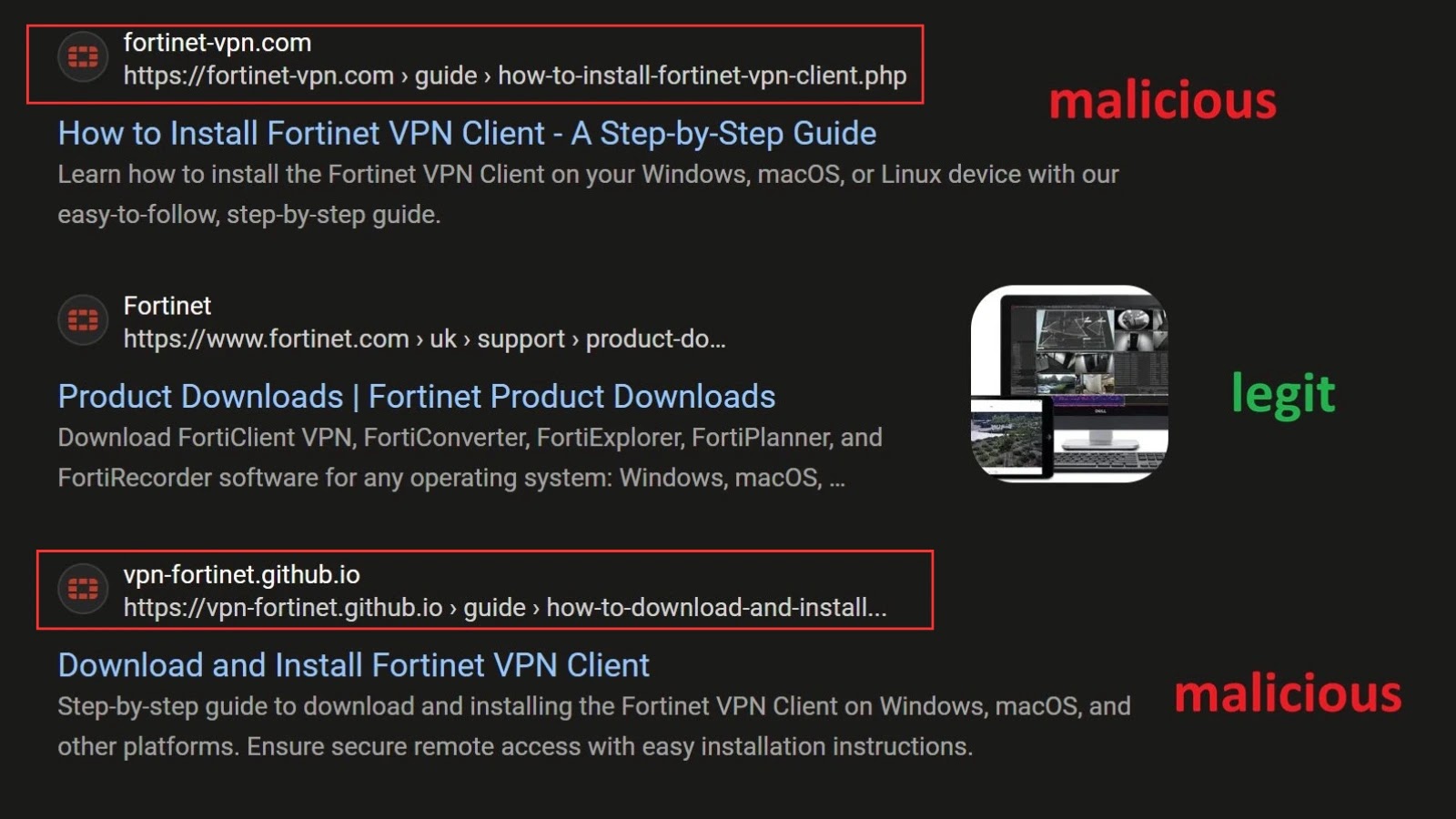
When customers seek for “Tips on how to obtain Fortinet VPN,” some AI summaries are scraping content material from the attacker’s malicious GitHub repository (vpn-fortinet[.]github[.]io) and presenting it as a professional step-by-step information.
Pretend Web sites in Search (Picture Credit: G0njxa)
As a result of the preliminary hyperlink is hosted on GitHub, a good platform, AI fashions and customers alike usually tend to belief the supply. This “hallucinated” belief leads customers to click on the hyperlink, initiating the assault chain.
How the Assault Works
The assault follows a intelligent, segmented circulate designed to filter out safety bots and goal solely actual human customers coming from particular search engines like google.
The Decoy Touchdown: The person clicks a hyperlink pointing to vpn-fortinet[.]github[.]io. This web page hosts a script that checks the “referrer” (the web site the person got here from).
Selective Redirects: If the person is visiting from a serious search engine like Google, Bing, Yahoo, or DuckDuckGo, the script routinely redirects them to the precise phishing web site: fortinet-vpn[.]com. If a safety crawler or direct customer accesses the web page with out these referrers, the redirect might not set off, hiding the malicious intent.
Credential Harvesting: The vacation spot web site completely mimics the professional Fortinet design. Earlier than permitting a obtain, it creates a faux modal popup asking the person to enter their “Distant Gateway,” “Login,” and “Password” to “configure” the installer.
Popup to steal login (Picture Credit: G0njxa)
The Bait: As soon as the sufferer submits their credentials, sending them on to the attackers, the location initiates a obtain from myfiles2[.]obtain. To keep away from suspicion, this payload typically installs a professional model of FortiClient, leaving the sufferer unaware that their entry credentials have been compromised.
Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
IT directors ought to instantly block the next domains and examine any inner visitors that has communicated with them.
IoC TypeValueDescriptionRedirect Domainvpn-fortinet[.]github[.]ioInitial touchdown web page hosted on GitHub Pages to evade popularity filters.Phishing URLfortinet-vpn[.]comThe vacation spot web site the place credential harvesting happens.Payload Hostmyfiles2[.]downloadHosting area for the decoy or malware payload.
Organizations should remind staff that professional software program downloads hardly ever require pre-authentication credentials simply to get the installer. Authenticity ought to at all times be verified by checking the URL bar for the official fortinet.com area.
Moreover, this marketing campaign highlights a crucial new threat: Don’t blindly belief AI search summaries. Whereas handy, these instruments ingest information from the open internet and may simply be manipulated by risk actors utilizing fundamental web optimization techniques. At all times confirm the supply hyperlink earlier than clicking.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X for day by day cybersecurity updates. Contact us to function your tales.