Microsoft’s current patch for the BadSuccessor vulnerability (CVE-2025-53779) has efficiently closed the direct privilege escalation path, however safety researchers warn that the underlying method stays viable for stylish attackers.
Whereas the patch prevents instant Area Admin escalation by means of one-sided delegated Managed Service Account (dMSA) hyperlinks, risk actors can nonetheless exploit the basic mechanics for credential harvesting and lateral motion in compromised Lively Listing environments.
Key Takeaways1. CVE-2025-53779 patch enforces mutual dMSA–account hyperlinks on the KDC, blocking one-sided privilege escalations.2. dMSA mechanics nonetheless allow credential grabs and dumps.2. Mitigate by patching servers.
The BadSuccessor vulnerability initially allowed low-privileged customers to realize immediate Area Admin privileges by abusing Home windows Server 2025’s new dMSA account sort.
By making a managed dMSA and linking it to high-privilege accounts, attackers might inherit each efficient privileges and Kerberos keys with out requiring group membership modifications or unique tooling.
The method exploited how the Key Distribution Middle (KDC) handled linked dMSAs as successors throughout authentication, merging goal privileges into the dMSA’s Privilege Attribute Certificates (PAC) and returning credential packages containing the goal’s authentication keys.
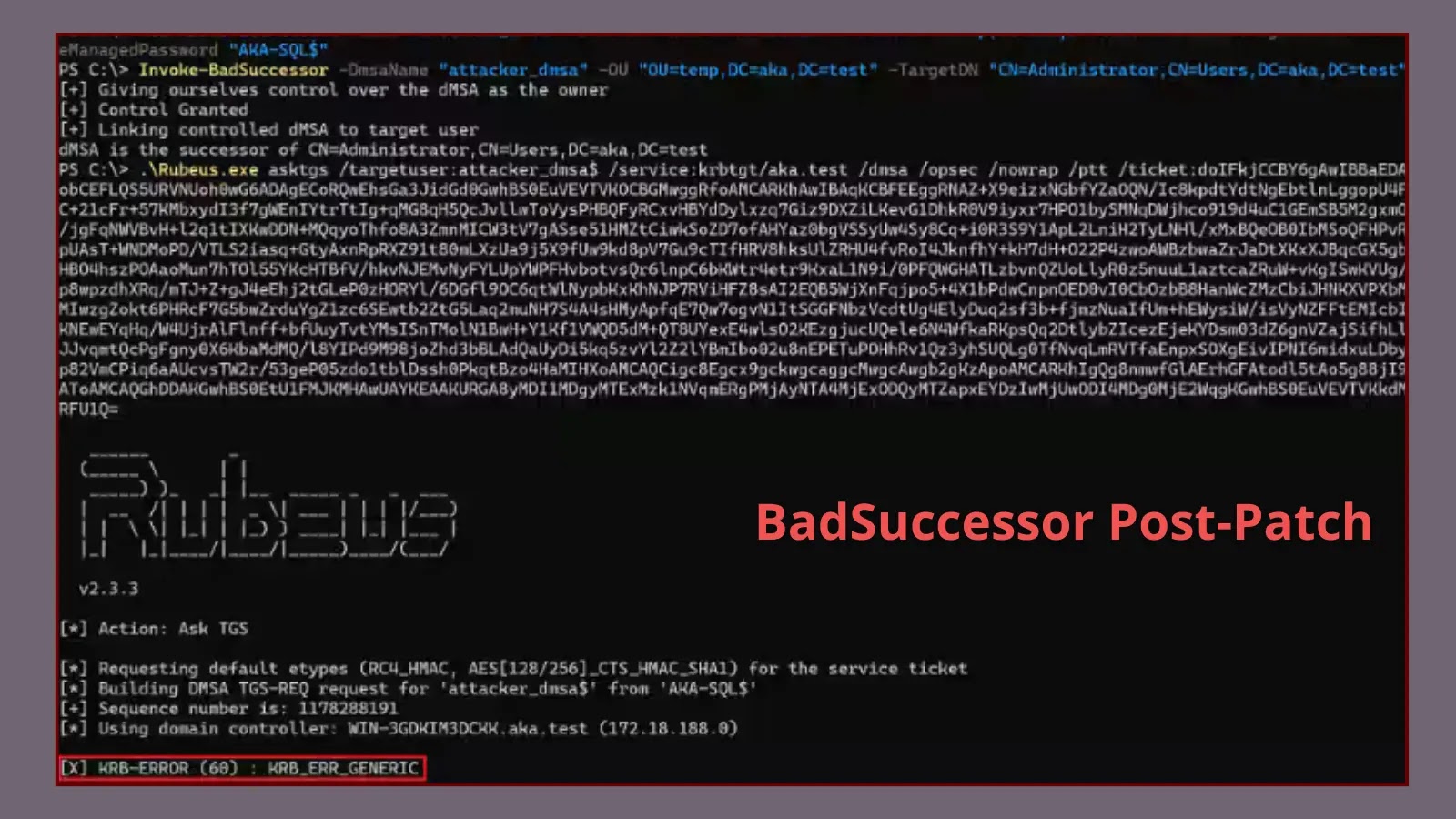
BadSuccessor Publish-Patch
Microsoft’s patch implementation focuses on KDC-level validation fairly than directory-side attribute safety.
Akamai reviews that the kdcsvc.dll modifications now require mutual linking between dMSA and goal accounts, mirroring reliable migration patterns.
Nonetheless, this enforcement mechanism nonetheless permits two important assault primitives that defenders should monitor. The primary primitive permits credential and privilege acquisition as an alternative choice to shadow credential assaults.
When attackers management each a goal principal and a dMSA, they will set up a mutual pairing to request dMSA tickets.
Error when authenticating a dMSA with a one-sided link- — failure happens at ticket issuance
This strategy presents a number of benefits: appearing with goal privileges whereas utilizing dMSA id for evasion, acquiring goal keys extra reliably than Kerberoasting assaults, and producing completely different telemetry signatures centered on hyperlink modifications and Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) issuance to the dMSA.
The second primitive gives a DCSync various for credential dumping in already-compromised domains.
Quite than utilizing conventional replication-based methods, attackers can leverage BadSuccessor mechanics to extract principal keys by means of regular ticket issuance processes.
This strategy generates distinct behavioral signatures which will bypass current detection mechanisms designed for typical credential dumping strategies.
Mitigations
Detection methods ought to deal with System Entry Management Lists (SACLs) auditing for dMSA creation and migration hyperlink attribute modifications.
Behavioral indicators embody repeated dMSA password fetch makes an attempt inside brief timeframes, enabled customers unexpectedly linked to dMSAs, and beforehand disabled accounts receiving new dMSA associations.
Organizations ought to prioritize patching Home windows Server 2025 area controllers whereas reviewing organizational unit permissions and tightening dMSA delegation controls to Tier 0 directors solely.
The evolution of BadSuccessor from vulnerability to persistent method highlights a broader trade problem the place patches shut particular exploitation paths whereas underlying assault mechanics stay exploitable.
Safety groups should adapt their monitoring and detection capabilities to account for these developed risk vectors, recognizing that refined attackers will proceed leveraging dMSA relationships for credential acquisition and lateral motion even in patched environments.
Discover this Story Attention-grabbing! Observe us on LinkedIn and X to Get Extra On the spot Updates.