A important vulnerability in eSIM know-how permits attackers to clone cellular subscriber profiles and hijack cellphone identities.
AG Safety Analysis revealed they broke the safety of Kigen eUICC playing cards with GSMA client certificates, marking what they declare is the primary profitable public hack in opposition to client GSMA eUICC and EAL-certified GSMA safety chips.
The analysis staff extracted personal ECC keys from compromised eUICC playing cards and demonstrated the flexibility to obtain eSIM profiles from main cellular community operators, together with AT&T, Vodafone, O2, Orange, and T-Cell, in cleartext format.
Key Takeaways1. Researchers efficiently hacked Kigen eUICC playing cards, extracting personal keys and downloading eSIM profiles from main carriers in unencrypted format.2. Reside checks demonstrated full cellphone identification hijacking, with attackers intercepting all calls, SMS, and two-factor authentication codes undetected.3. The vulnerability impacts over 2 billion SIMs, permitting one compromised certificates to entry any cellular operator’s eSIM profiles globally.4. Kigen deployed safety patches to tens of millions of eSIMs whereas GSMA shut down check profiles and up to date business safety specs.
This breakthrough represents a major safety breach within the eSIM ecosystem, which processes over 2 billion SIMs enabled by Kigen’s safe SIM OS, in line with firm press releases.
Java Card Flaw Permits Distant Cloning
The assault exploits elementary flaws in Java Card Digital Machine implementation, particularly concentrating on kind confusion vulnerabilities much like points reported in 2019.
The researchers developed a Proof of Idea that mimics malicious applet set up over the OTA SMS-PP protocol (Brief Message Service Level to Level).
The vulnerability permits attackers to bypass a number of safety mechanisms, together with EAL4/5 certification, side-channel assault countermeasures, and Java Card Runtime security measures.
The assault vector requires both bodily entry to the goal card together with information of set up keys or distant exploitation via OTA channels.
Important technical components compromised embrace community operators’ OPc keys and Authentication Administration Subject (AMF) – two important secret keys embedded in eSIM profiles that needs to be “safeguarded by community operators at any value”.
The researchers’ toolkit implements a Primary Safety Test (BSC) command that evaluates Java Card-capable eUICC safety via varied bytecode vulnerability assessments.
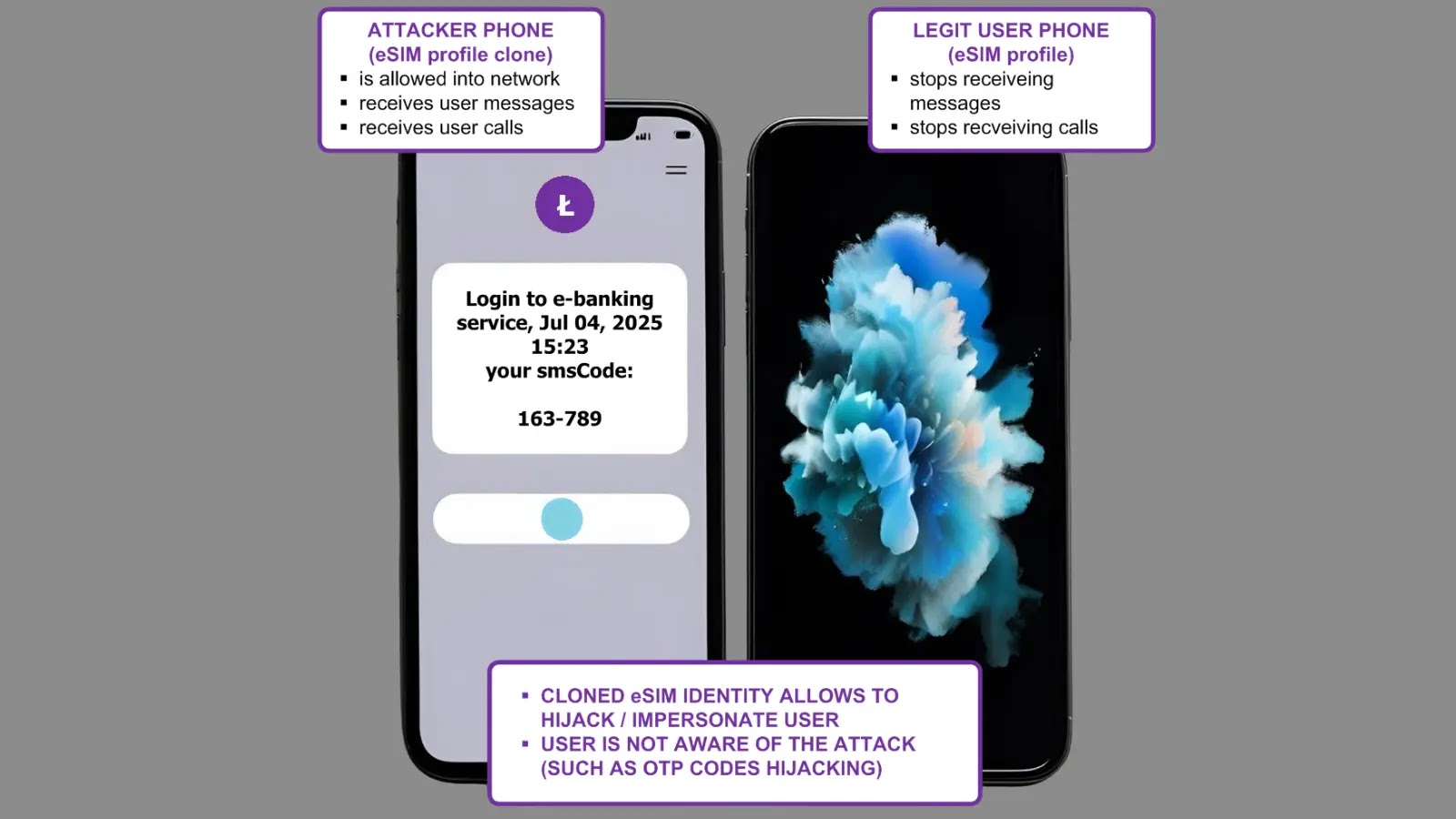
Probably the most alarming demonstration concerned profitable eSIM cloning checks carried out on Orange Poland’s community in July 2025.
Researchers put in equivalent Orange eSIM profiles on two completely different bodily eUICC playing cards and demonstrated full subscriber identification hijacking.
When the malicious system was activated, it instantly started receiving all calls and SMS messages meant for the reputable subscriber.
This cloning functionality poses extreme dangers for two-factor authentication techniques, as attackers can intercept SMS-based verification codes for providers like Gmail and e-banking platforms.
The researchers confirmed that reputable customers stay unaware of the hijacking, as no seen hint seems on the consumer finish.
Kigen has responded by implementing kind security checks throughout roughly 180 JavaCard bytecode directions and coordinating with GSMA to replace the TS.48 Generic Check Profile specification.
The corporate distributed patches to tens of millions of eSIMs and issued a safety bulletin detailing mitigation methods.
GSMA has additionally revealed new software notes and shut down all check profiles to forestall unauthorized Java Card software installations.
Examine reside malware habits, hint each step of an assault, and make sooner, smarter safety selections -> Attempt ANY.RUN now