A complicated phishing equipment dubbed Tykit, which impersonates Microsoft 365 login pages to reap company credentials.
First detected in Could 2025, the equipment has surged in exercise throughout September and October, exploiting SVG information as a stealthy supply mechanism.
Not like fundamental phishing lures, Tykit demonstrates maturity by constant obfuscation methods and multi-stage command-and-control (C2) interactions, making it a potent device for credential theft throughout world organizations.
The equipment’s rise aligns with a broader spike in SVG-based assaults, the place seemingly innocuous picture information embed JavaScript payloads. These scripts use XOR encoding to rebuild malicious code, which executes through the damaging eval() operate to redirect victims to pretend login websites.
Cybersecurity agency ANY.RUN has recognized Tykit, a mature phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) equipment that impersonates Microsoft 365 login pages to seize company credentials by adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) methods.
Tykit Phishing Equipment Mimics Microsoft 365 Login
Tykit emerged in sandbox environments in early Could 2025, with researchers pivoting from a single suspicious SVG (SHA256: a7184bef39523bef32683ef7af440a5b2235e83e7fb83c6b7ee5f08286731892) to over 189 associated periods.
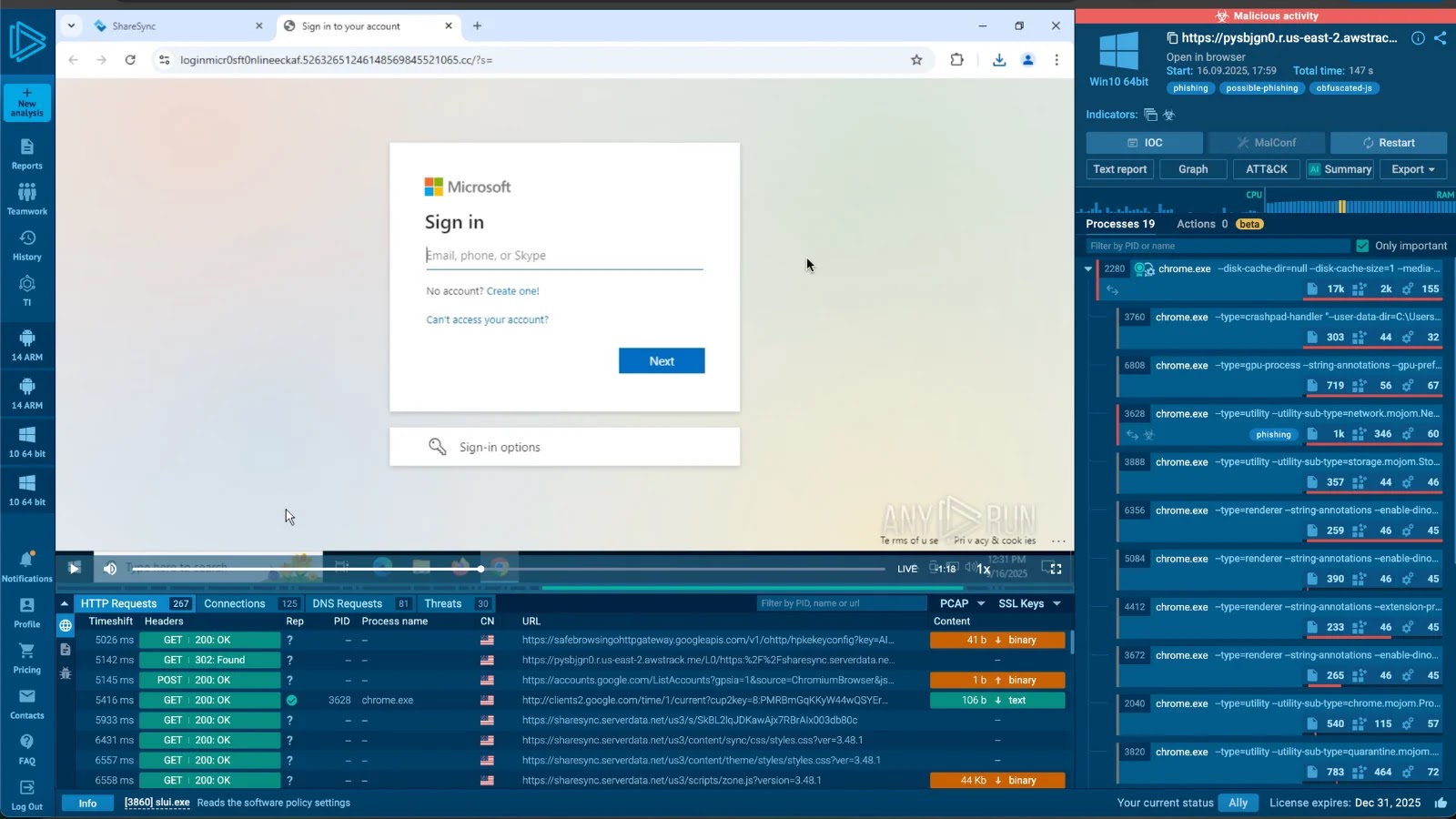
Domains like loginmicr0sft0nlineeckaf[.]52632651246148569845521065[.]cc host the phishing pages, usually appending Base64-encoded sufferer emails through the “?s=” parameter. Exfiltration targets servers on segy[.]cc variants, sending staged POST requests to /api/validate and /api/login.
This infrastructure spans templated domains resembling domain-generation algorithms, with patterns like ^loginmicr(o|0)s.?.([a-z]+)?d+.cc$ for phishing hosts and ^segy?. for C2.
The equipment’s consistency, unchanged client-side logic, and obfuscation counsel organized operators distributing it extensively, evading detection by fundamental anti-debugging like blocking developer instruments and context menus.
Tykit’s circulation begins with an SVG prompting a pretend “telephone quantity test,” which accepts any enter to proceed.
The method begins by sending you to a CAPTCHA web page that makes use of Cloudflare Turnstile to dam bots. After that, it masses a web page that appears like Microsoft 365. Within the background, it checks emails utilizing JSON knowledge, which incorporates session keys and redirects.
Upon credential entry, obfuscated JavaScript exfiltrates knowledge to /api/login, together with expired JWT tokens for authenticity.
Server responses dictate outcomes: success renders benign HTML to masks theft, errors present “incorrect password” prompts, and “data” standing triggers logging to /x.php. This adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) setup bypasses fundamental MFA, stealing emails, passwords, and tokens in JSON format.
Cyber threats hit various sectors, together with building, IT, finance, authorities, telecom, actual property, and training, primarily within the US, Canada, LATAM, EMEA, Southeast Asia, and the Center East.
Compromises allow account takeovers, knowledge exfiltration from SaaS apps, and lateral motion, posing dangers of regulatory fines and belief erosion.
To counter it, organizations ought to examine SVG content material with sandboxing and content material disarmament, undertake phishing-resistant MFA like FIDO2, and monitor IOCs akin to eval() calls, Base64 parameters, and suspicious domains.
SIEM guidelines for /api/validate patterns, mixed with consumer coaching on anomalous “pictures,” can disrupt campaigns early. As phishing evolves, Tykit underscores the necessity for proactive risk searching to remain forward of those “typical” but efficient kits.
Broaden Your Menace Protection with Recent IOCs from real-time Cyberthreats => Strive Now