An ongoing malicious promoting marketing campaign is weaponizing authentic software program downloads to deploy OysterLoader malware, beforehand recognized as Broomstick and CleanUpLoader.
This subtle preliminary entry device permits cybercriminals to determine footholds in company networks, in the end serving as a supply mechanism for the infamous Rhysida ransomware gang.
The Rhysida ransomware operation has focused enterprises since rising from the Vice Society group in 2021, later rebranding in 2023. Regardless of makes an attempt to evade regulation enforcement by means of title adjustments, safety researchers proceed monitoring their evolving techniques.
The present marketing campaign uncovered by Expel represents their second main malvertising operation, constructing on techniques confirmed profitable throughout their preliminary run from Might to September 2024. Since June 2025, risk actors have maintained persistent operations with dramatically elevated depth and scope.
Rhysida’s Evolution and Persistent Menace
Rhysida operators buy ads on Bing’s search engine, directing unsuspecting customers towards convincing however malicious touchdown pages.
These sponsored outcomes seem prominently in search outcomes and even inside Home windows 11 begin menu searches, inserting malware downloads immediately earlier than potential victims.
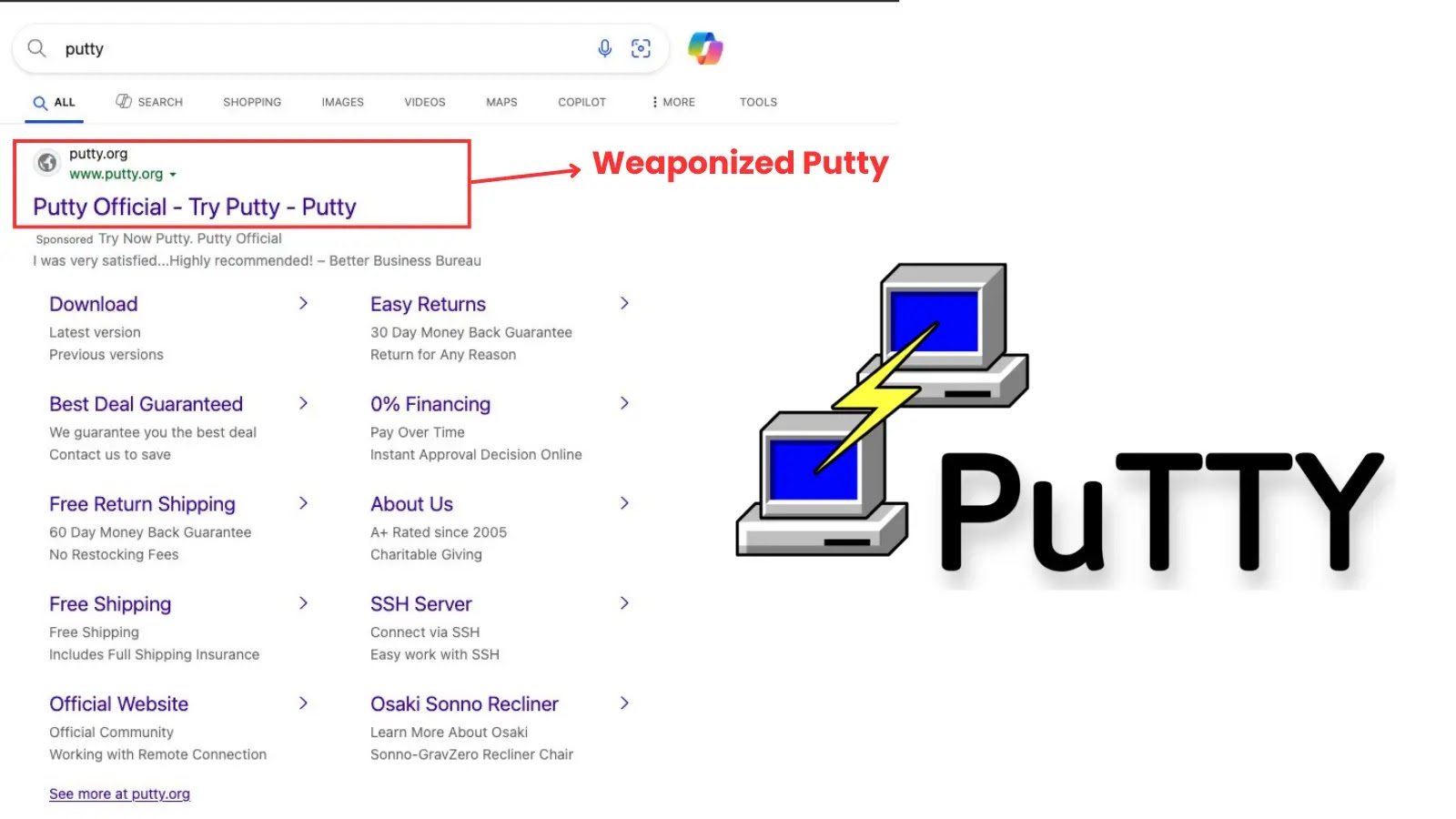
Latest campaigns have impersonated in style software program, together with Microsoft Groups, PuTTY, and Zoom, with risk actors creating practically equivalent pretend obtain pages.
Bing advertisements exhibiting up within the Home windows 11 begin menu, that one result’s sponsored and misspells PuTTy as “Putty”
The malicious PuTTY ads reveal this method, with sponsored outcomes deliberately misspelling “PuTTY” as “Putty” whereas showing authentic sufficient to deceive customers looking for the genuine distant entry device.
OysterLoader’s effectiveness stems from two main evasion strategies. First, attackers pack the malware by means of compression and obfuscation, hiding its true capabilities from safety instruments.
This ends in remarkably low preliminary detection charges, with fewer than 5 antivirus engines sometimes flagging new samples. Second, risk actors make use of code-signing certificates, exploiting Home windows belief mechanisms to seem authentic.
Resulting from their obfuscation, it could actually take a number of days earlier than extra AV engines flag the malware
The dimensions of this operation is obvious in certificates utilization. Whereas the 2024 marketing campaign utilized seven certificates, the present 2025 marketing campaign has burned by means of over 40 distinctive code-signing certificates, indicating substantial useful resource funding and operational dedication.
Rhysida doesn’t rely solely on OysterLoader. Expel researchers found the gang concurrently deploying Latrodectus malware, confirmed when equivalent code-signing certificates appeared on each malware households.
Moreover, Rhysida has exploited Microsoft’s Trusted Signing service, circumventing its 72-hour certificates validity restrictions. Microsoft experiences revoking over 200 certificates related to this marketing campaign, but operations stay lively.
Safety groups ought to stay vigilant in opposition to malvertising campaigns and confirm software program downloads solely by means of official channels to keep away from compromise.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X for every day cybersecurity updates. Contact us to function your tales.