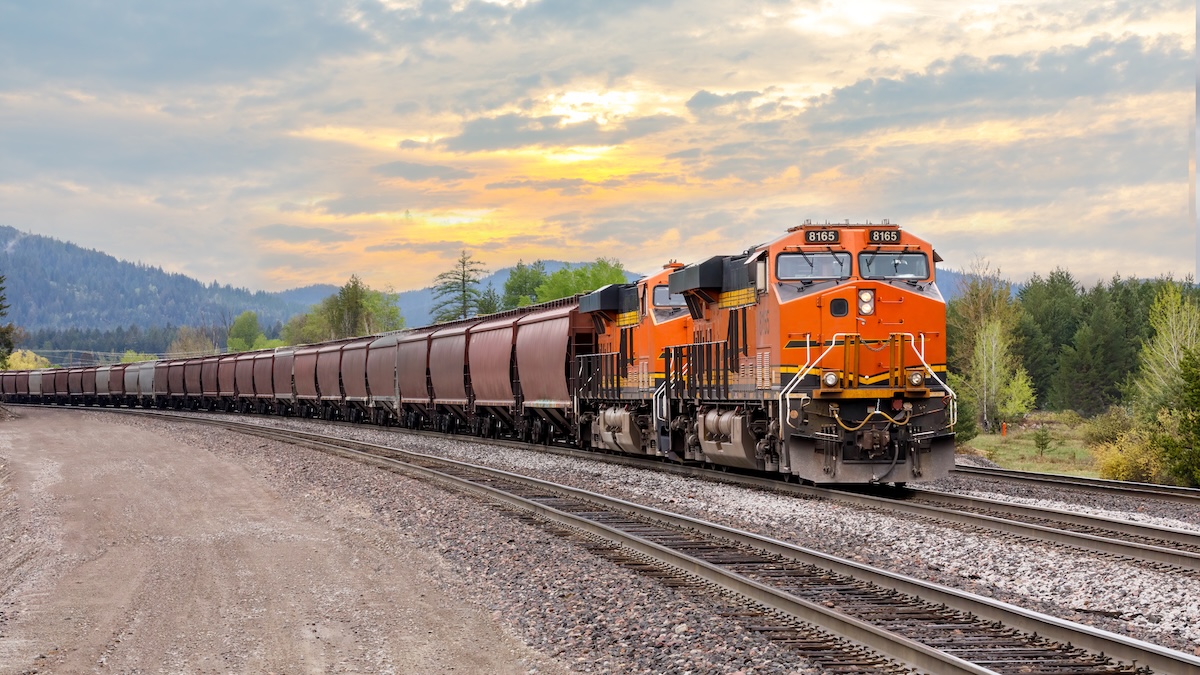
The US cybersecurity company CISA has disclosed a vulnerability that may be exploited to control or tamper with a practice’s brakes.
CISA final week printed an advisory describing CVE-2025-1727, a difficulty affecting the distant linking protocol utilized by techniques referred to as Finish-of-Practice and Head-of-Practice.
An Finish-of-Practice (EoT) machine, also referred to as a Flashing Rear Finish Machine (FRED), is positioned on the finish of a practice, being designed to transmit information to a tool within the locomotive named the Head-of-Practice (HoT). The system, launched to interchange the caboose, is used to acquire standing information from the tip of the practice (significantly helpful for lengthy freight trains), however it could possibly additionally obtain instructions to use the brakes on the rear of the practice.
The issue, in line with CISA’s advisory, is that the protocol remotely linking the EoT and HoT over radio indicators shouldn’t be safe (no authentication or encryption are used), enabling an attacker to make use of specifically crafted packets transmitted with a software-defined radio to ship instructions to the EoT machine.
“Profitable exploitation of this vulnerability might enable an attacker to ship their very own brake management instructions to the end-of-train machine, inflicting a sudden stoppage of the practice which can result in a disruption of operations, or induce brake failure,” CISA mentioned.
The company has credited researchers Neil Smith and Eric Reuter for locating the vulnerability. Smith shared further particulars and context for CVE-2025-1727 on Friday in a publish on X.
Smith mentioned he found the difficulty in 2012 throughout a time when he was doing industrial management system (ICS) safety analysis with ICS-CERT, a predecessor of CISA. The researcher and ICS-CERT tried over the following a number of years to work with the Affiliation of American Railroads (AAR) to get the vulnerability mounted, however they failed to succeed in a consensus.
Smith mentioned the AAR had needed the impression of the vulnerability to be confirmed in the true world moderately than solely in lab environments, which was tough to do because of the potential penalties.Commercial. Scroll to proceed studying.
“You can remotely take management over a practice’s brake controller from a really lengthy distance away, utilizing {hardware} that prices sub $500. You can induce brake failure resulting in derailments or you might shut down all the nationwide railway system,” Smith mentioned, including that the weak gadgets are additionally current on passenger trains.
The disagreement between the researcher and AAR culminated in 2016, when the Boston Evaluation printed an article primarily based on Smith’s findings, accusing the rail trade of risking security over earnings. Just a few days later, the AAR disputed Smith’s claims, saying the article was primarily based on inaccuracies and mischaracterizations.
Eric Reuter, the second researcher credited by CISA for locating the vulnerability, found the difficulty in 2018 and disclosed technical particulars on the DEF CON convention. Once more, no motion was taken by the AAR, in line with Smith.
As well as, Smith mentioned he not too long ago realized that the identical weak spot was really first found and reported to the AAR 20 years in the past, in 2005.
The researcher mentioned the advisory printed by CISA final week is the results of him resubmitting his findings in 2024. The company allegedly reached out to impacted distributors and the AAR and the difficulty was once more downplayed, however the AAR finally introduced that it might be taking motion.
CISA’s advisory, which notes that there is no such thing as a proof of exploitation within the wild, factors out that the requirements committee in command of the protocol is conscious of the vulnerability and on the lookout for mitigations, whereas the AAR is “pursuing new gear and protocols which ought to exchange conventional Finish-of-Practice and Head-of-Practice gadgets”.
A current press launch reveals that roughly 25,000 HoT and 45,000 EoT gadgets will have to be upgraded, with the method anticipated to start in 2026.
The cybersecurity trade has lengthy warned about trains being weak to hacker assaults and the risk isn’t just theoretical. Each direct and oblique cyberattacks prompted disruptions to railway techniques lately.
In a 2023 incident, 20 trains have been disrupted in Poland because of a hack involving broadcasting radio instructions that instructed trains to cease. That assault relied on a easy hack leveraging the truth that management indicators might be transmitted to trains over a identified, unencrypted radio frequency.
SecurityWeek has reached out to the AAR for remark and can replace this text if the group responds.
Associated: Police Are Probing a Cyberattack on Wi-Fi Networks at UK Practice Stations