A safety weak spot has been disclosed within the synthetic intelligence (AI)-powered code editor Cursor that would set off code execution when a maliciously crafted repository is opened utilizing this system.
The problem stems from the truth that an out-of-the-box safety setting is disabled by default, opening the door for attackers to run arbitrary code on customers’ computer systems with their privileges.
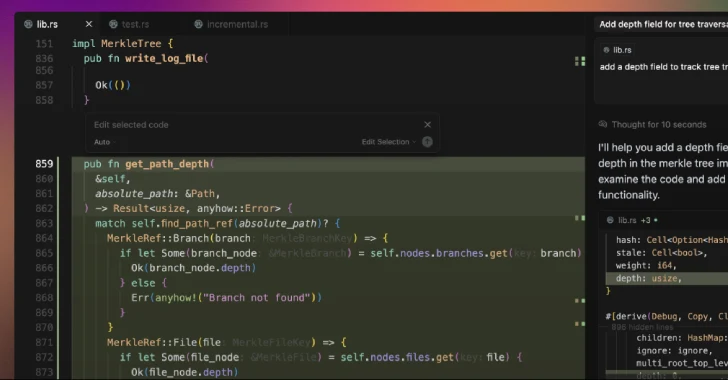
“Cursor ships with Workspace Belief disabled by default, so VS Code-style duties configured with runOptions.runOn: ‘folderOpen’ auto-execute the second a developer browses a challenge,” Oasis Safety mentioned in an evaluation. “A malicious .vscode/duties.json turns an informal ‘open folder’ into silent code execution within the consumer’s context.”
Cursor is an AI-powered fork of Visible Studio Code, which helps a function known as Workspace Belief to permit builders to securely browse and edit code no matter the place it got here from or who wrote it.
With this selection disabled, an attacker could make obtainable a challenge in GitHub (or any platform) and embody a hidden “autorun” instruction that instructs the IDE to execute a job as quickly as a folder is opened, inflicting malicious code to be executed when the sufferer makes an attempt to browse the booby-trapped repository in Cursor.
“This has the potential to leak delicate credentials, modify information, or function a vector for broader system compromise, inserting Cursor customers at important threat from provide chain assaults,” Oasis Safety researcher Erez Schwartz mentioned.
To counter this risk, customers are suggested to allow Office Belief in Cursor, open untrusted repositories in a distinct code editor, and audit them earlier than opening them within the software.
The event comes as immediate injections and jailbreaks have emerged as a stealthy and systemic risk plaguing AI-powered coding and reasoning brokers like Claude Code, Cline, K2 Suppose, and Windsurf, permitting risk actors to embed malicious directions in sneaky methods to trick the methods into performing malicious actions or leaking information from software program improvement environments.
Software program provide chain safety outfit Checkmarx, in a report final week, revealed how Anthropic’s newly launched automated safety opinions in Claude Code might inadvertently expose tasks to safety dangers, together with instructing it to disregard weak code by way of immediate injections, inflicting builders to push malicious or insecure code previous safety opinions.
“On this case, a fastidiously written remark can persuade Claude that even plainly harmful code is totally secure,” the corporate mentioned. “The tip consequence: a developer – whether or not malicious or simply attempting to close Claude up – can simply trick Claude into considering a vulnerability is secure.”
One other downside is that the AI inspection course of additionally generates and executes take a look at circumstances, which might result in a state of affairs the place malicious code is run in opposition to manufacturing databases if Claude Code is not correctly sandboxed.
The AI firm, which additionally just lately launched a brand new file creation and enhancing function in Claude, has warned that the function carries immediate injection dangers because of it operating in a “sandboxed computing setting with restricted web entry.”
Particularly, it is doable for a nasty actor to “inconspicuously” add directions by way of exterior information or web sites – aka oblique immediate injection – that trick the chatbot into downloading and operating untrusted code or studying delicate information from a data supply related by way of the Mannequin Context Protocol (MCP).
“This implies Claude could be tricked into sending info from its context (e.g., prompts, tasks, information by way of MCP, Google integrations) to malicious third events,” Anthropic mentioned. “To mitigate these dangers, we suggest you monitor Claude whereas utilizing the function and cease it in the event you see it utilizing or accessing information unexpectedly.”
That is not all. Late final month, the corporate additionally revealed browser-using AI fashions like Claude for Chrome can face immediate injection assaults, and that it has applied a number of defenses to handle the risk and scale back the assault success charge of 23.6% to 11.2%.
“New types of immediate injection assaults are additionally always being developed by malicious actors,” it added. “By uncovering real-world examples of unsafe habits and new assault patterns that are not current in managed assessments, we’ll educate our fashions to acknowledge the assaults and account for the associated behaviors, and make sure that security classifiers will choose up something that the mannequin itself misses.”
On the similar time, these instruments have additionally been discovered vulnerable to conventional safety vulnerabilities, broadening the assault floor with potential real-world affect –
A WebSocket authentication bypass in Claude Code IDE extensions (CVE-2025-52882, CVSS rating: 8.8) that would have allowed an attacker to connect with a sufferer’s unauthenticated native WebSocket server just by luring them to go to a web site below their management, enabling distant command execution
An SQL injection vulnerability within the Postgres MCP server that would have allowed an attacker to bypass the read-only restriction and execute arbitrary SQL statements
A path traversal vulnerability in Microsoft NLWeb that would have allowed a distant attacker to learn delicate information, together with system configurations (“/and so on/passwd”) and cloud credentials (.env information), utilizing a specifically crafted URL
An incorrect authorization vulnerability in Lovable (CVE-2025-48757, CVSS rating: 9.3) that would have allowed distant unauthenticated attackers to learn or write to arbitrary database tables of generated websites
Open redirect, saved cross-site scripting (XSS), and delicate information leakage vulnerabilities in Base44 that would have allowed attackers to entry the sufferer’s apps and improvement workspace, harvest API keys, inject malicious logic into user-generated functions, and exfiltrate information
A vulnerability in Ollama Desktop arising because of incomplete cross-origin controls that would have allowed an attacker to stage a drive-by assault, the place visiting a malicious web site can reconfigure the applying’s settings to intercept chats and even alter responses utilizing poisoned fashions
“As AI-driven improvement accelerates, essentially the most urgent threats are sometimes not unique AI assaults however failures in classical safety controls,” Imperva mentioned. “To guard the rising ecosystem of ‘vibe coding’ platforms, safety should be handled as a basis, not an afterthought.”