Nov 19, 2025Ravie LakshmananCyber Espionage / MalwareThe menace actor often called PlushDaemon has been noticed utilizing a beforehand undocumented Go-based community backdoor codenamed EdgeStepper to facilitate adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) assaults.
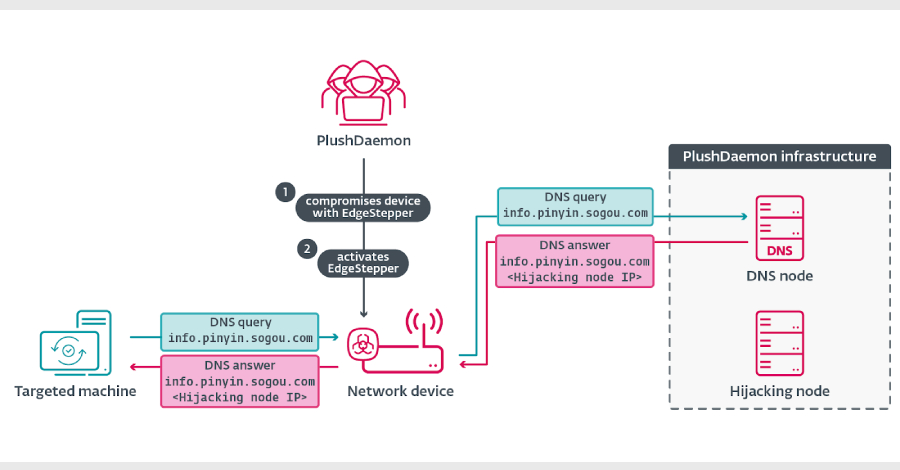
EdgeStepper “redirects all DNS queries to an exterior, malicious hijacking node, successfully rerouting the site visitors from authentic infrastructure used for software program updates to attacker-controlled infrastructure,” ESET safety researcher Facundo Muñoz mentioned in a report shared with The Hacker Information.
Identified to be energetic since no less than 2018, PlushDaemon is assessed to be a China-aligned group that has attacked entities within the U.S., New Zealand, Cambodia, Hong Kong, Taiwan, South Korea, and mainland China.
It was first documented by the Slovak cybersecurity firm earlier this January, detailing a provide chain assault aimed toward a South Korean digital personal community (VPN) supplier named IPany to focus on a semiconductor firm and an unidentified software program improvement firm in South Korea with a feature-rich implant dubbed SlowStepper.
Among the many adversary’s victims embrace a college in Beijing, a Taiwanese firm that manufactures electronics, an organization within the automotive sector, and a department of a Japanese firm within the manufacturing sector. Earlier this month, ESET additionally mentioned it noticed PlushDaemon focusing on two entities in Cambodia this yr, an organization within the automotive sector and a department of a Japanese firm within the manufacturing sector, with SlowStepper.
The first preliminary entry mechanism for the menace actor is to leverage AitM poisoning, a method that has been embraced by an “ever growing” variety of China-affiliated superior persistent menace (APT) clusters within the final two years, resembling LuoYu, Evasive Panda, BlackTech, TheWizards APT, Blackwood, and FontGoblin. ESET mentioned it is monitoring ten energetic China-aligned teams which have hijacked software program replace mechanisms for preliminary entry and lateral motion.
The assault basically commences with the menace actor compromising an edge community machine (e.g., a router) that its goal is probably going to hook up with. That is achieved by both exploiting a safety flaw within the software program or by way of weak credentials, permitting them to deploy caEdgeStepper.
“Then, EdgeStepper begins redirecting DNS queries to a malicious DNS node that verifies whether or not the area within the DNS question message is expounded to software program updates, and in that case, it replies with the IP deal with of the hijacking node,” Muñoz defined. “Alternatively, now we have additionally noticed that some servers are each the DNS node and the hijacking node; in these instances, the DNS node replies to DNS queries with its personal IP deal with.”
Internally, the malware consists of two shifting components: a Distributor module that resolves the IP deal with related to the DNS node area (“take a look at.dsc.wcsset[.]com”) and invokes the Ruler part chargeable for configuring IP packet filter guidelines utilizing iptables.
The assault particularly checks for a number of Chinese language software program, together with Sogou Pinyin, to have their replace channels hijacked by the use of EdgeStepper to ship a malicious DLL (“popup_4.2.0.2246.dll” aka LittleDaemon) from a menace actor-controlled server. A primary-stage deployed by way of hijacked updates, LittleDaemon is designed to speak with the attacker node to fetch a downloader known as DaemonicLogistics if SlowStepper is just not operating on the contaminated system.
The primary goal of DaemonicLogistics is to obtain the SlowStepper backdoor from the server and execute it. SlowStepper helps an intensive set of options to collect system data, information, browser credentials, extract knowledge from various messaging apps, and even uninstall itself.
“These implants give PlushDaemon the potential to compromise targets anyplace on the earth,” Muñoz mentioned.