Sep 08, 2025Ravie LakshmananMalvertising / Encryption
Cybersecurity researchers have detailed a brand new subtle malware marketing campaign that leverages paid advertisements on search engines like google and yahoo like Google to ship malware to unsuspecting customers searching for well-liked instruments like GitHub Desktop.
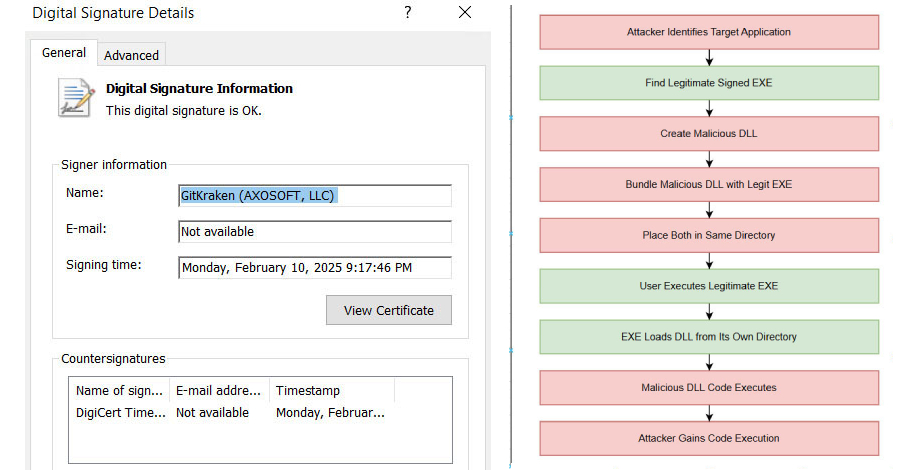
Whereas malvertising campaigns have develop into commonplace lately, the newest exercise offers it somewhat twist of its personal: Embedding a GitHub commit right into a web page URL containing altered hyperlinks that time to attacker-controlled infrastructure.
“Even when a hyperlink appears to level to a good platform similar to GitHub, the underlying URL could be manipulated to resolve to a counterfeit website,” Arctic Wolf stated in a report printed final week.
Completely focused IT and software program improvement corporations inside Western Europe since at the least December 2024, the hyperlinks inside the rogue GitHub commit are designed to funnel customers to a malicious obtain hosted on a lookalike area (“gitpage[.]app”).
The primary-stage malware delivered utilizing poisoned search outcomes is a bloated 128 MB Microsoft Software program Installer (MSI) that, owing to its measurement, evades most present on-line safety sandboxes, whereas a Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)-gated decryption routine retains the payload encrypted on methods and not using a actual GPU. The approach has been codenamed GPUGate.
“Methods with out correct GPU drivers are more likely to be digital machines (VMs), sandboxes, or older evaluation environments that safety researchers generally use,” the cybersecurity firm stated. “The executable […] makes use of GPU features to generate an encryption key for decrypting the payload, and it checks the GPU gadget title because it does this.”
Moreover incorporating a number of rubbish information as a filler and complicating evaluation, it additionally terminates execution if the gadget title is lower than 10 characters or GPU features usually are not obtainable.
The assault subsequently entails the execution of a Visible Primary Script that launches a PowerShell script, which, in flip, runs with administrator privileges, provides Microsoft Defender exclusions, units up scheduled duties for persistence, and eventually runs executable information extracted from a downloaded ZIP archive.
The top objective is to facilitate data theft and ship secondary payloads, whereas concurrently evading detection. It is assessed that the menace actors behind the marketing campaign have native Russian language proficiency, given the presence of Russian language feedback within the PowerShell script.
Additional evaluation of the menace actor’s area has revealed it to be appearing as a staging floor for Atomic macOS Stealer (AMOS), suggesting a cross-platform method.
“By exploiting GitHub’s commit construction and leveraging Google Advertisements, menace actors can convincingly mimic authentic software program repositories and redirect customers to malicious payloads – bypassing each consumer scrutiny and endpoint defenses,” Arctic Wolf.
The disclosure comes as Acronis detailed the continuing evolution of a trojanized ConnectWise ScreenConnect marketing campaign that makes use of the distant entry software program to drop AsyncRAT, PureHVNC RAT, and a customized PowerShell-based distant entry trojan (RAT) on contaminated hosts in social engineering assaults geared toward U.S. organizations since March 2025.
The bespoke PowerShell RAT, executed by way of a JavaScript file downloaded from the cracked ScreenConnect server, offers some primary functionalities similar to operating applications, downloading and executing information, and a easy persistence mechanism.
“Attackers now use a ClickOnce runner installer for ScreenConnect, which lacks embedded configuration and as an alternative fetches elements at runtime,” the safety vendor stated. “This evolution makes conventional static detection strategies much less efficient and complicates prevention, leaving defenders with few dependable choices.”