Aug 24, 2025Ravie LakshmananMalware / Provide Chain Safety
Cybersecurity researchers have found a malicious Go module that presents itself as a brute-force software for SSH however really incorporates performance to discreetly exfiltrate credentials to its creator.
“On the primary profitable login, the bundle sends the goal IP handle, username, and password to a hard-coded Telegram bot managed by the risk actor,” Socket researcher Kirill Boychenko mentioned.
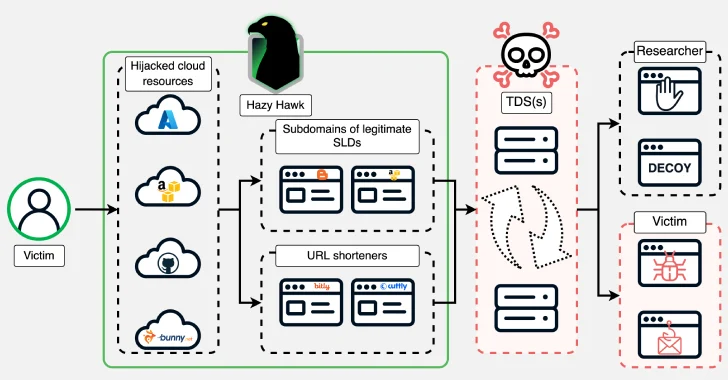
The misleading bundle, named “golang-random-ip-ssh-bruteforce,” has been linked to a GitHub account referred to as IllDieAnyway (G3TT), which is at present now not accessible. Nonetheless, it continues to be out there on pkg.go[.]dev. It was printed on June 24, 2022.
The software program provide chain safety firm mentioned the Go module works by scanning random IPv4 addresses for uncovered SSH providers on TCP port 22, then making an attempt to brute-force the service utilizing an embedded username-password record and exfiltrating the profitable credentials to the attacker.
A notable facet of the malware is that it intentionally disables host key verification by setting “ssh.InsecureIgnoreHostKey” as a HostKeyCallback, thereby permitting the SSH consumer to just accept connections from any server no matter their id.
The wordlist is pretty simple, together with solely two usernames root and admin, and pairing them in opposition to weak passwords like root, check, password, admin, 12345678, 1234, qwerty, webadmin, webmaster, techsupport, letmein, and Passw@rd.
The malicious code runs in an infinite loop to generate the IPv4 addresses, with the bundle making an attempt concurrent SSH logins from the wordlist.
The main points are transmitted to a risk actor-controlled Telegram bot named “@sshZXC_bot” (ssh_bot) through the API, which then acknowledges the receipt of the credentials. The messages are despatched via the bot to an account with the deal with “@io_ping” (Gett).
An Web Archive snapshot of the now-removed GitHub account exhibits that IllDieAnyway, aka G3TT’s software program portfolio, included an IP port scanner, an Instagram profile information and media parser, and even a PHP-based command-and-control (C2) botnet referred to as Selica-C2.
Their YouTube channel, which stays accessible, hosts numerous short-form movies on “Methods to hack a Telegram bot” and what they declare to be the “strongest SMS bomber for the Russian Federation,” which might ship spam SMS texts and messages to VK customers utilizing a Telegram bot. It is assessed that the risk actor is of Russian origin.
“The bundle offloads scanning and password guessing to unwitting operators, spreads threat throughout their IPs, and funnels the successes to a single risk actor-controlled Telegram bot,” Boychenko mentioned.
“It disables host key verification, drives excessive concurrency, and exits after the primary legitimate login to prioritize fast seize. As a result of the Telegram Bot API makes use of HTTPS, the site visitors appears like regular internet requests and might slip previous coarse egress controls.”