Ravie LakshmananJan 28, 2026Vulnerability / Workflow Automation
Cybersecurity researchers have disclosed two new safety flaws within the n8n workflow automation platform, together with a vital vulnerability that might end in distant code execution.
The weaknesses, found by the JFrog Safety Analysis group, are listed under –
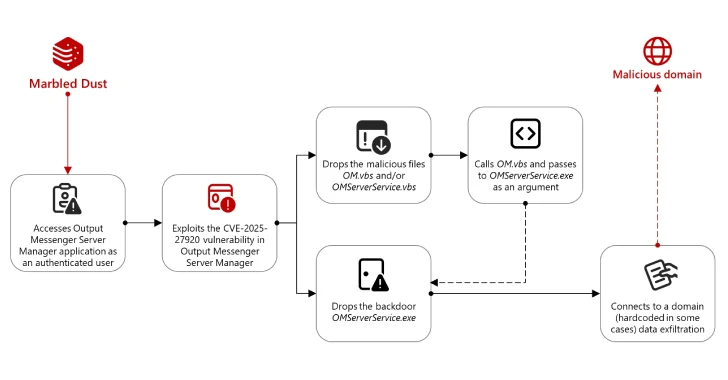
CVE-2026-1470 (CVSS rating: 9.9) – An eval injection vulnerability that might permit an authenticated consumer to bypass the Expression sandbox mechanism and obtain full distant code execution on n8n’s primary node by passing specifically crafted JavaScript code
CVE-2026-0863 (CVSS rating: 8.5) – An eval injection vulnerability that might permit an authenticated consumer to bypass n8n’s python-task-executor sandbox restrictions and run arbitrary Python code on the underlying working system
Profitable exploitation of the issues might allow an attacker to hijack a complete n8n occasion, together with beneath eventualities the place it is working beneath “inside” execution mode. In its documentation, n8n notes that utilizing inside mode in manufacturing environments can pose a safety danger, urging customers to change to exterior mode to make sure correct isolation between n8n and activity runner processes.
“As n8n spans a complete group to automate AI workflows, it holds the keys to core instruments, features, and knowledge from infrastructure, together with LLM APIs, gross sales knowledge, and inside IAM methods, amongst others,” JFrog mentioned in a press release shared with The Hacker Information. “This ends in escapes giving a hacker an efficient “skeleton key” to the whole company.”
To deal with the issues, customers are suggested to replace to the next variations –
CVE-2026-1470 – 1.123.17, 2.4.5, or 2.5.1
CVE-2026-0863 – 1.123.14, 2.3.5, or 2.4.2
The event comes merely weeks after Cyera Analysis Labs detailed a maximum-severity safety flaw in n8n (CVE-2026-21858 aka Ni8mare) that enables an unauthenticated distant attacker to achieve full management over inclined situations.
“These vulnerabilities spotlight how troublesome it’s to securely sandbox dynamic, excessive‑stage languages reminiscent of JavaScript and Python,” researcher Nathan Nehorai mentioned. “Even with a number of validation layers, deny lists, and AST‑primarily based controls in place, delicate language options and runtime behaviors will be leveraged to bypass safety assumptions.”
“On this case, deprecated or not often used constructs, mixed with interpreter modifications and exception dealing with conduct, have been sufficient to interrupt out of in any other case restrictive sandboxes and obtain distant code execution.”