A severe security flaw in Dell RecoverPoint for Virtual Machines has been actively exploited as a zero-day vulnerability since mid-2024. This was revealed in a report by Google Mandiant and Google Threat Intelligence Group, which attributes the attacks to a China-linked threat cluster identified as UNC6201.
Details of the Vulnerability
The flaw, tracked as CVE-2026-22769 with a CVSS score of 10.0, involves hard-coded credentials in versions before 6.0.3.1 HF1. It allows unauthorized access to the system, granting root-level persistence. Dell has confirmed that other products like RecoverPoint Classic are unaffected.
To mitigate the risk, Dell advises upgrading affected versions and recommends deploying RecoverPoint within a secure, internally controlled network environment. The vulnerability particularly targets versions 5.3 SP4 P1 through 6.0 SP3 P1, necessitating specific upgrade paths to version 6.0.3.1 HF1.
Exploitation Techniques
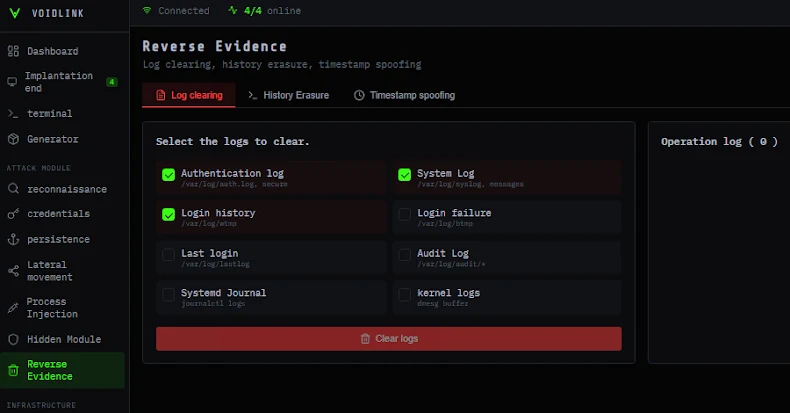
The attack exploits an “admin” user in the Apache Tomcat Manager, allowing the deployment of a web shell named SLAYSTYLE to execute commands as root. This leads to the installation of the BRICKSTORM backdoor and its successor, GRIMBOLT, which is harder to detect due to its advanced features.
GRIMBOLT enhances its stealth capabilities, making it difficult for traditional detection methods to identify the threat. The campaign primarily targets organizations in North America, focusing on systems lacking endpoint detection and response capabilities.
Broader Implications and Future Outlook
UNC6201 shows similarities with another espionage group, UNC5221, known for exploiting virtualization technologies. Despite these overlaps, they are considered separate entities. The group employs tactics like using “Ghost NICs” to hide their tracks and manipulate network interfaces.
The persistent threat underscores the challenges in securing systems against nation-state actors, who often target vulnerabilities before patches are available. Recent activities by groups like Volt Typhoon highlight the ongoing risks to critical infrastructure sectors, emphasizing the need for vigilant cybersecurity measures.
Organizations are urged to stay informed about potential threats and ensure their systems are updated with the latest patches to defend against such sophisticated cyber-attacks.