A important vulnerability in OpenClaw, the open-source AI private assistant trusted by over 100,000 builders, has been found and weaponized right into a devastating one-click distant code execution exploit.
Safety researchers at depthfirst Common Safety Intelligence uncovered a logic flaw that, when mixed with different vulnerabilities, may set off a series response.
Permits attackers to achieve full management of sufferer methods through a single malicious hyperlink, requiring no consumer interplay.
Vulnerability Overview: Technical Assault Mechanics
OpenClaw’s structure grants AI brokers “god mode” entry to messaging apps, API keys, and unrestricted management of the native pc.
Whereas neighborhood enthusiasm surrounding the platform has pushed fast adoption, the safety margin for error in such a high-privilege surroundings turns into razor-thin.
AttributeDetailsProductOpenClaw (previously ClawdBot/Moltbot)Vulnerability TypeUnsafe URL Parameter Dealing with + Cross-Web site WebSocket HijackingImpactUnauthenticated Distant Code Execution with System-Degree AccessCVSS ScoreCritical (9.8+)Assault VectorNetwork (Single Malicious Hyperlink)
The newly disclosed vulnerability exploits three distinct parts working in sequence: unsafe URL parameter ingestion, rapid gateway connection with out validation, and computerized transmission of authentication tokens.
The exploitation chain begins with three seemingly benign operations occurring independently throughout the codebase.
The app-settings.ts module blindly accepts the gatewayUrl question parameter from the URL with out validation, then shops it instantly in localStorage.
Upon setting the applying, the app-lifecycle.ts instantly triggers connectGateway(), which robotically bundles the security-sensitive authToken into the connection handshake to the attacker-controlled gateway server.
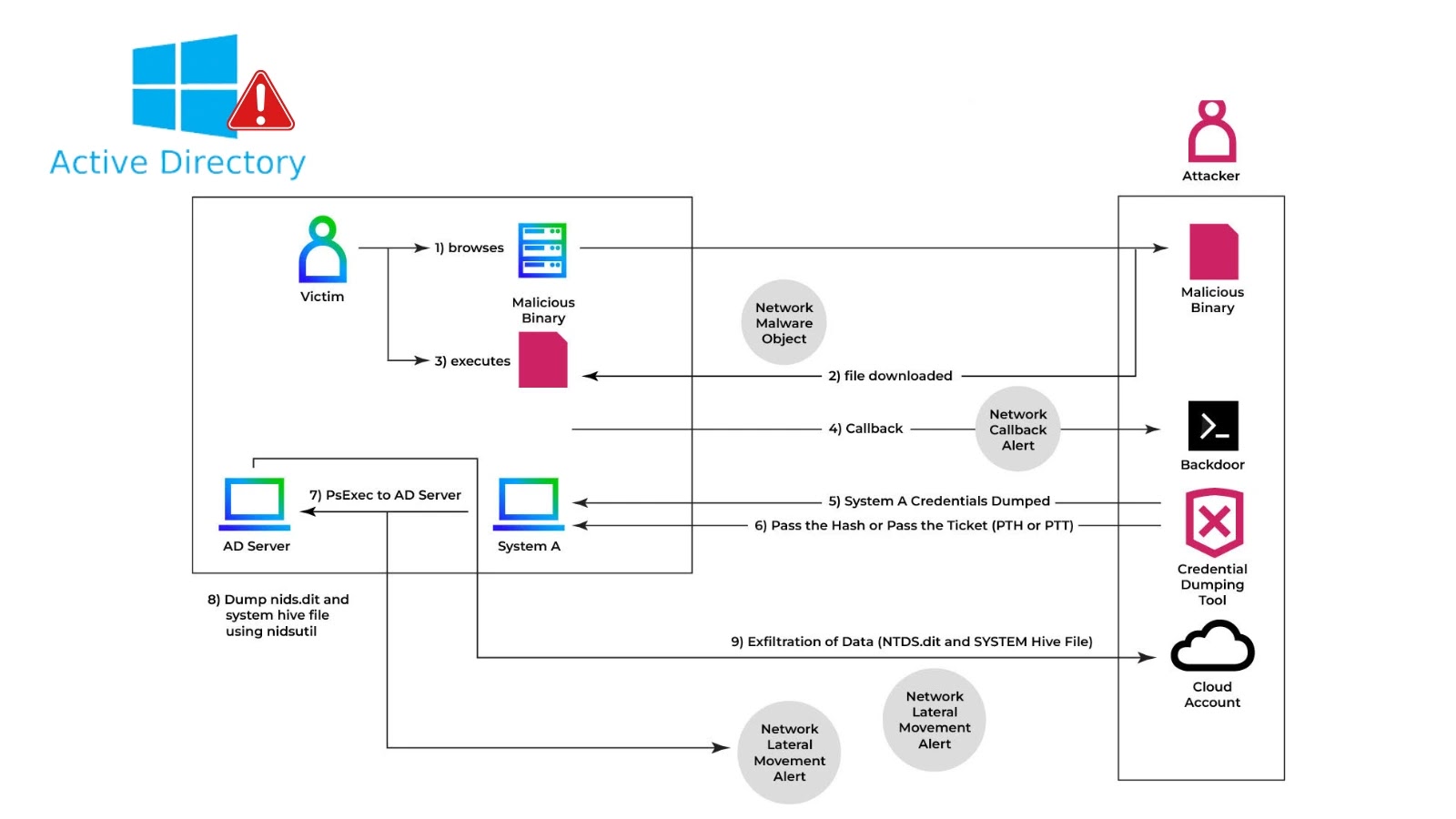
1-Click on RCE Exploit Kill Chain supply: depthfirst)
This sample creates a important info disclosure vulnerability. The kill chain exploits a further WebSocket origin validation flaw.
StageDescriptionVisitUser lands on malicious web site.LoadJS masses OpenClaw with malicious gatewayUrl.LeakauthToken despatched to attacker.ConnectWebSocket opened to localhost.BypassSafety guardrails disabled.ExecuteAttacker runs arbitrary instructions.
When victims go to a malicious webpage, attacker-injected JavaScript executes inside their browser context, establishing an area connection to the sufferer’s OpenClaw occasion working on localhost:18789.
In contrast to customary HTTP connections, browser WebSocket implementations don’t implement Similar-Origin Coverage protections; as a substitute, they depend on server-side origin header validation, which OpenClaw omits solely.
This Cross-Web site WebSocket Hijacking (CSWSH) allows the attacker to pivot via the sufferer’s browser as a proxy.
As soon as authenticated through the stolen token, the attacker leverages the operator. admin and operator roles. approvals, and scopes to show off security mechanisms.
An exec. approvals.set request turns off consumer affirmation prompts, whereas a config. patch request units instruments.exec.host to “gateway,” forcing command execution instantly on the host machine slightly than inside containerized sandboxes.
The ultimate payload invokes node. invoke with arbitrary bash instructions, reaching full system compromise.
Mitigations
The OpenClaw growth crew quickly addressed the vulnerability by implementing a gateway URL affirmation modal, eliminating the auto-connect with out immediate habits that enabled the assault.
DepthFirst advises all customers working variations earlier than v2026.1.24-1 stay susceptible and will improve instantly.
Directors ought to rotate authentication tokens and audit command execution logs for suspicious exercise.
This incident underscores the safety dangers inherent in granting AI brokers unrestricted system entry with out sturdy validation of configuration modifications and community connections.
Organizations deploying OpenClaw ought to implement further community segmentation, limit outbound WebSocket connections from AI agent processes, and preserve strict audit logging for authentication token utilization and privilege modifications.
Observe us on Google Information, LinkedIn, and X for each day cybersecurity updates. Contact us to function your tales.