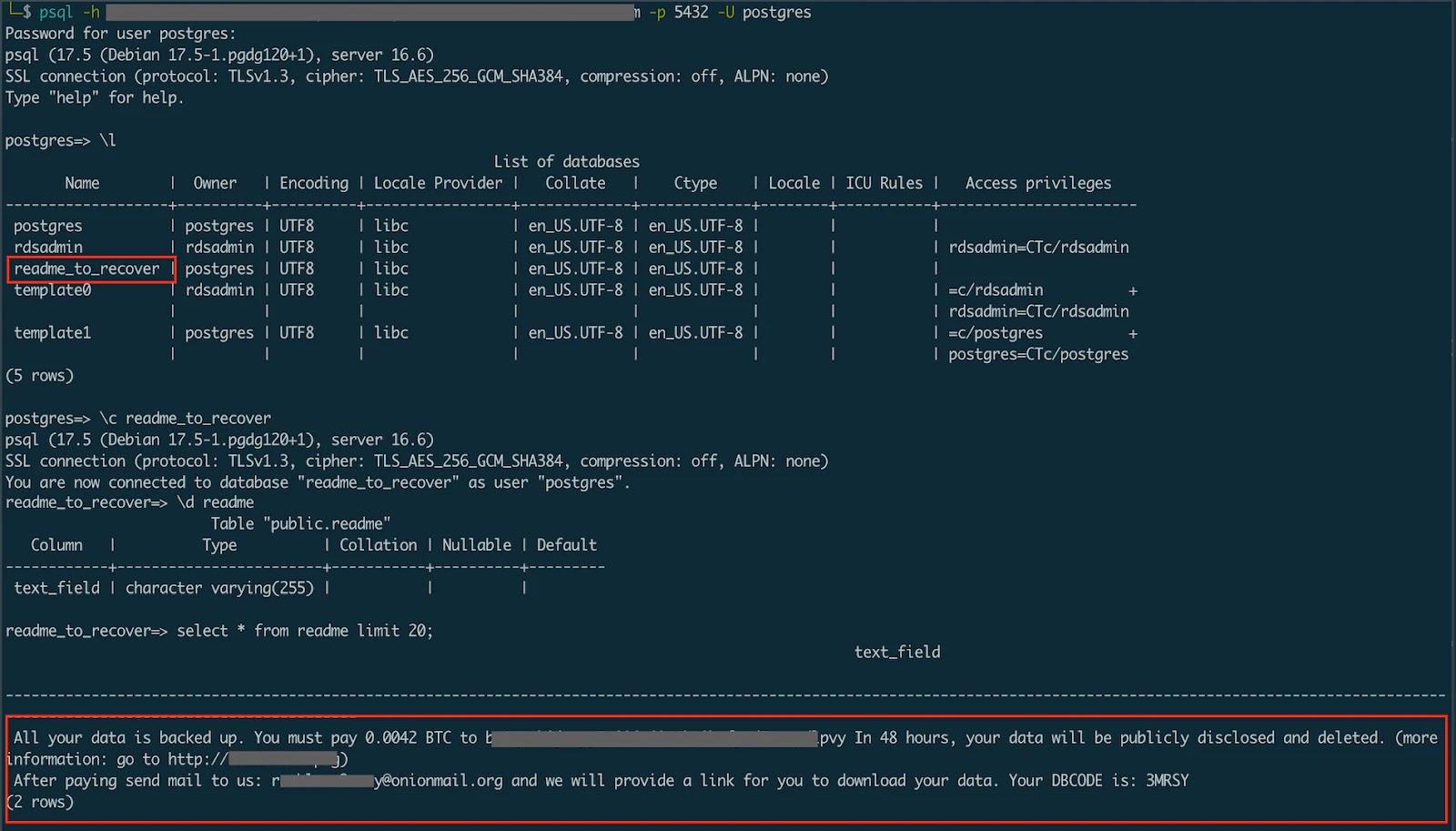
In a revealing cybersecurity incident from September 2025, investigators uncovered a rogue virtual machine (VM) operating within a VMware vSphere environment. This discovery was closely linked to the notorious cyber group Muddled Libra, also known as Scattered Spider and UNC3944. The group’s tactics involved using the VM as a covert staging host, facilitating network reconnaissance, tool deployment, and eventual data exfiltration.
Intrusion Tactics and Techniques
Muddled Libra is known for its adept social engineering methods, including techniques like smishing and vishing, to impersonate employees. This strategy often coerces help desks into resetting passwords or bypassing multi-factor authentication. Rather than relying heavily on malware, this group prefers to exploit legitimate administrative tools and the victim’s infrastructure to mask their presence.
According to Palo Alto Networks, attackers breached the vSphere system mere hours after initial access. They created a new VM titled “New Virtual Machine,” signifying the start of their infiltration. The attackers then obtained stolen certificates to forge authentication tickets, extending their control over the network.
Exploitation of Network Resources
The cyber operatives powered down virtualized domain controllers, accessing and copying critical files such as NTDS.dit and SYSTEM onto the rogue VM. This maneuver was part of their broader strategy to gather directory information using ADRecon and investigate service principal names. Their reach extended to the victim’s Snowflake environment, and they attempted to extract mailbox data off-network using file-sharing services and S3 Browser.
To maintain persistence, the attackers established a secure shell (SSH) tunnel using Chisel, a tool delivered via a ZIP file named goon.zip from an AWS S3 bucket under their control. Network logs indicated continuous traffic to an attacker-controlled address over TCP 443 for approximately 15 hours, mimicking standard HTTPS traffic.
Preventive Measures and Recommendations
Security experts recommend enhancing identity controls and enforcing the principle of least privilege for vSphere and administrative accounts to mitigate risks. Monitoring for suspicious VM creations, unexpected domain controller shutdowns, and unusual VMDK mounts is crucial. Additionally, vigilance is required for detecting unusual use of common tools and anomalous outbound traffic on port 443 from new systems.
By implementing these measures, organizations can better counteract the living-off-the-land tactics of cyber groups like Muddled Libra before they result in widespread lateral movement and severe data breaches.
Stay updated with the latest in cybersecurity by following us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X. Set CSN as your preferred source on Google for instant updates.