Microsoft has revealed a sophisticated variation of the ClickFix attack, leveraging Domain Name System (DNS) lookups to stage malware. This attack uses the ‘nslookup’ command, executed via the Windows Run dialog, to download malicious payloads. Targeting users through phishing, malvertising, and drive-by downloads, ClickFix has become a prevalent method for cybercriminals to trick victims into compromising their systems.
Understanding the ClickFix Tactic
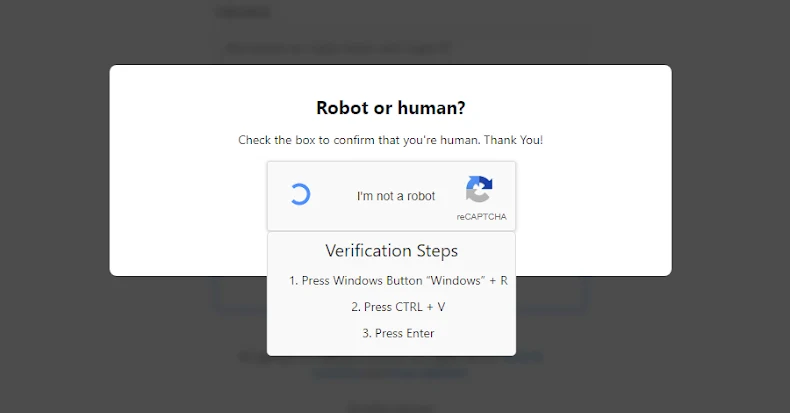
ClickFix has gained traction over the past two years as attackers manipulate users into executing commands on their machines. The approach often involves directing users to deceptive webpages that mimic CAPTCHA verifications or suggest resolving non-existent issues. Once the command is executed, the malware is downloaded, enabling attackers to bypass traditional security measures easily.
Microsoft’s Threat Intelligence team highlighted that the latest DNS-based variation initiates a command through cmd.exe, performing a DNS lookup against an external server. The response is used to trigger the next stage of the attack, illustrating the tactic’s ability to blend malicious activities into standard network traffic.
The Role of DNS in Malware Distribution
Utilizing DNS as a communication channel, attackers can discreetly interact with their infrastructure, adding a validation layer before executing secondary payloads. By minimizing reliance on conventional web requests, this method camouflages the attack within normal activities, making it harder for security solutions to detect.
The malicious payload executes an attack chain that includes downloading a ZIP file from an external server, containing a Python script that conducts reconnaissance and deploys additional malware. This script eventually initiates ModeloRAT, a Python-based remote access trojan, ensuring persistent access through a Windows shortcut file.
Broader Implications and Emerging Threats
Bitdefender has observed a rise in Lumma Stealer activities linked to ClickFix-style attacks, particularly those involving fake CAPTCHA campaigns. These methods often employ CastleLoader, a malware loader used by the threat actor GrayBravo, to infiltrate systems. Despite law enforcement efforts in 2025, Lumma Stealer operations have shown resilience, adapting to alternative methods and hosting providers.
Moreover, several campaigns have emerged, utilizing social engineering to deploy various stealers and loaders. Attackers exploit phishing, malvertising, and even AI platforms to spread malware. A notable macOS campaign employs Odyssey Stealer, targeting cryptocurrency users by exfiltrating sensitive data from browser wallets.
These developments underscore the need for vigilance, as attackers continuously refine their strategies. The DNS-based ClickFix attack highlights the evolving landscape of cyber threats and the importance of robust security practices to counteract these sophisticated methods.